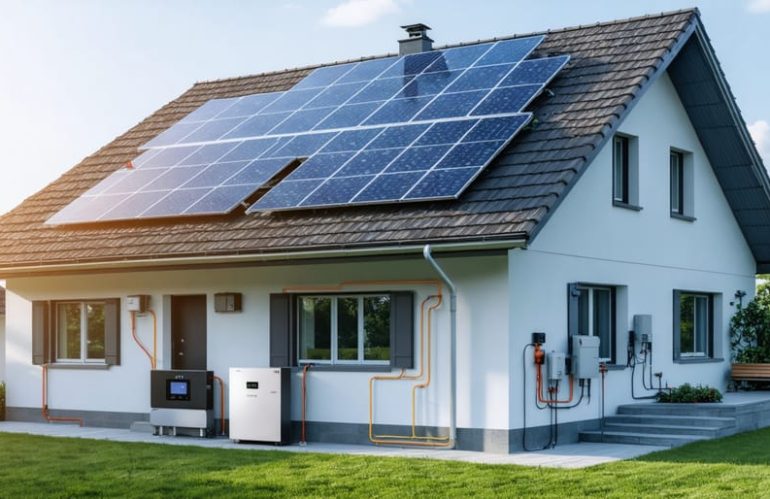
Understanding your home’s solar power system starts with mastering its core components and their interconnections. A residential solar monitoring system diagram reveals the elegant simplicity behind this powerful technology. From roof-mounted panels capturing sunlight to inverters converting DC power into usable AC electricity, each element plays a crucial role in powering your home sustainably. This visual roadmap helps homeowners optimize their system’s performance, troubleshoot potential issues, and maximize energy production throughout the year. Whether you’re a new solar adopter or considering the switch to clean energy, understanding your system’s diagram empowers you to take control of your home’s energy future while reducing both your carbon footprint and monthly utility bills.
Understanding Your Solar System’s Components
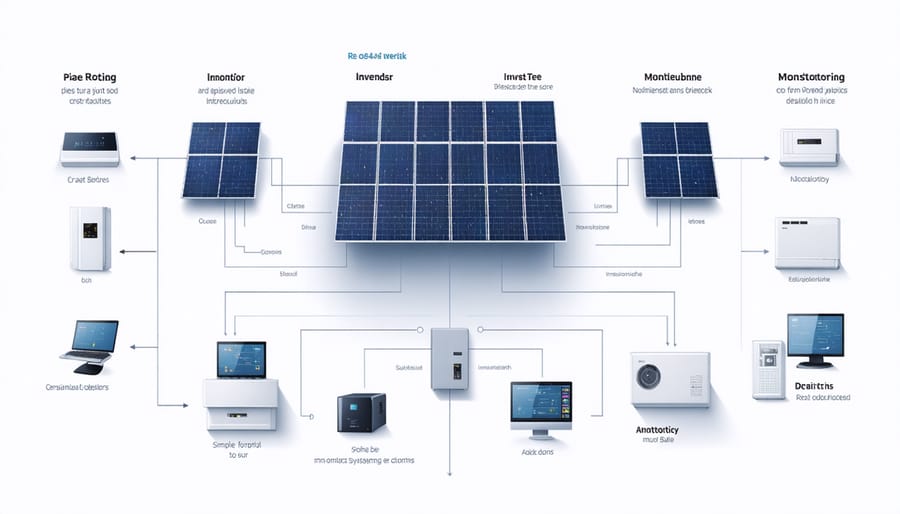
Solar Panels and Arrays
Solar panels are typically arranged in rows on your roof, positioned to maximize sunlight exposure throughout the day. These panels can be connected in two main configurations: series (string) or parallel. In a series connection, panels are linked end-to-end like a chain, increasing voltage while maintaining the same current. Parallel connections combine panels side-by-side, keeping voltage constant while increasing current output.
Most residential installations use a combination of both configurations, creating what’s called a string-parallel arrangement. This setup provides optimal power production while maintaining system reliability. The number and layout of panels depend on your roof space, energy needs, and local sunshine patterns. Modern arrays often include power optimizers or microinverters for each panel, allowing individual panel monitoring and better performance when parts of the array are shaded.
Inverters and Power Conditioning
Inverters play a crucial role in your solar power system by converting the DC electricity generated by your solar panels into AC power that your home can use. Think of it as a translator that makes solar energy speak the same language as your household appliances. Most modern inverters are highly efficient, converting about 95-98% of the incoming power.
Beyond simple conversion, these devices also condition the power to ensure it’s stable and safe for your electronics. They automatically shut off if there’s a power outage (for safety reasons) and provide real-time monitoring of your system’s performance. Many of today’s inverters come with smart features that let you track energy production through your smartphone, helping you maximize your solar investment.
You might encounter different types of inverters: string inverters for simple installations, microinverters for more complex setups, or hybrid inverters that work with battery storage systems.
Monitoring Equipment and Sensors
Modern solar systems come equipped with smart monitoring devices that help you track your system’s performance in real-time. The main monitoring components include production meters, which measure how much electricity your panels generate, and consumption meters that track your home’s energy usage. Most systems feature a central monitoring gateway that connects to your home’s internet, allowing you to access performance data through user-friendly mobile apps or web portals. Temperature sensors on panels and inverters help detect any overheating issues, while voltage sensors ensure optimal power output. These monitoring tools typically display daily energy production, cost savings, and even environmental impact metrics. Many systems can also send automatic alerts if performance drops, helping you quickly identify and address any maintenance needs.
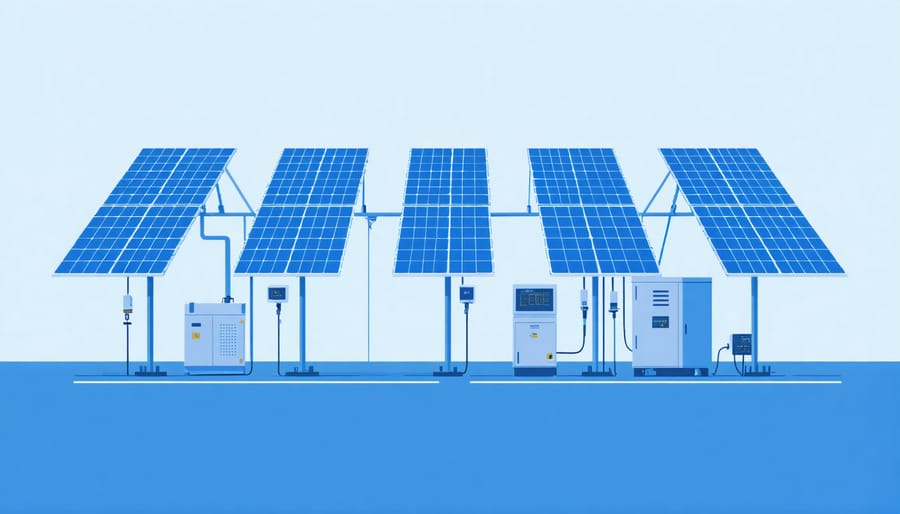

Key Monitoring Points in Your Solar System
Panel Performance Indicators
Modern solar panels come equipped with sophisticated monitoring systems that help homeowners track their system’s performance. The most crucial indicators include voltage monitoring, current output, and temperature readings. These measurements are typically displayed on your inverter’s digital screen or through a user-friendly mobile app.
Your system’s voltage tells you how efficiently electricity flows through the panels, while current measurements show the actual amount of power being produced. Temperature monitoring is equally important, as panels perform best between 59-95°F (15-35°C). When temperatures rise above this range, efficiency can decrease by 0.5% for each degree increase.
Most modern solar installations include smart sensors at key points: directly on the panels, at the inverter connection, and at the main electrical panel. These monitoring points work together to give you real-time performance data and alert you to any potential issues before they become problems. This allows you to ensure your system is operating at peak efficiency and helps identify when maintenance might be needed.
System Connection Points
Your solar system connects to your home and the grid through several crucial points that ensure safe and efficient operation. The main service panel, often called the breaker box, serves as the central hub where solar power integrates with your home’s electrical system. A dedicated solar disconnect switch provides an important safety feature, allowing you to quickly cut power from the panels when needed.
The system also includes a net meter that tracks energy flow between your home and the power grid. This smart device measures both the electricity you draw from the utility company and the excess power your panels send back, ensuring accurate billing and credits.
For monitoring purposes, most modern systems include a junction box with built-in sensors that track performance data. These sensors connect to your home’s internet through a monitoring gateway, allowing you to check your system’s output through a smartphone app or web portal.
Safety features include ground fault protection and surge protection devices, which protect both your solar equipment and home appliances from electrical anomalies. These connection points are typically housed in weather-resistant enclosures to ensure durability and reliable operation year-round.
Power Output Measurement
Modern residential solar systems come equipped with sophisticated monitoring capabilities that let you track your power production in real-time. Through a user-friendly app or web portal, you can view your system’s daily, monthly, and annual energy output. These monitoring systems display easy-to-understand graphs and charts showing how much electricity your panels generate throughout the day and how much money you’re saving. Many systems also alert you to potential issues or maintenance needs, ensuring optimal performance. You can compare your actual production against expected output based on weather conditions and panel specifications, helping you verify that your system is working efficiently. This data helps you make informed decisions about your energy usage and provides peace of mind that your investment is paying off.
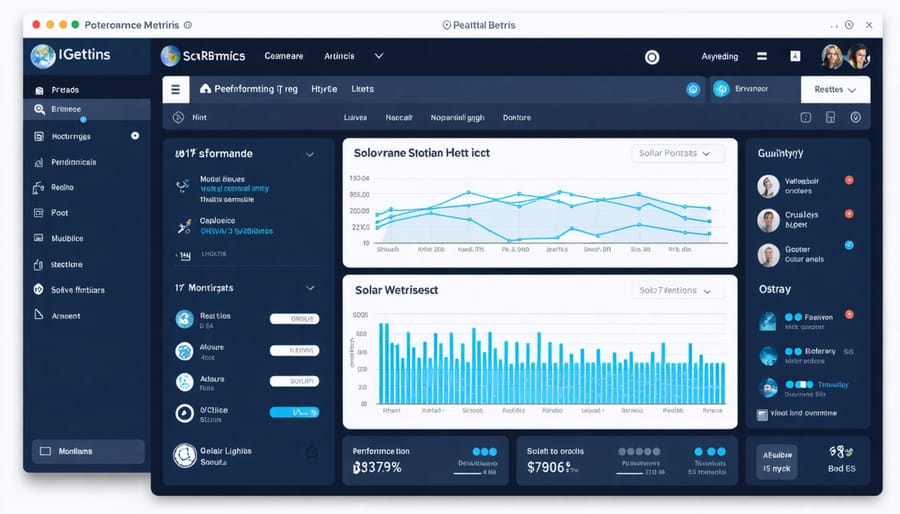
Reading Your System’s Health Dashboard
Normal Operating Parameters
A well-functioning residential solar system typically produces power that aligns with your home’s daytime electricity needs. During peak sunlight hours (usually 10 AM to 2 PM), your system should generate its maximum rated output, which for most homes ranges between 4-8 kilowatts per hour. Your inverter’s display should show a steady power flow during these times, with normal fluctuations based on cloud cover and seasonal changes.
The system voltage should maintain a stable range between 220-240V for standard residential setups. Your solar panels should operate at temperatures between 15-35°C (59-95°F) for optimal efficiency, though they can safely function outside this range. Panel efficiency typically ranges from 15-22%, depending on the type and quality of your installation.
Performance monitoring should show consistent daily generation patterns that peak at midday, forming a bell curve on your monitoring graphs. Monthly energy production usually varies by season, with summer months typically generating 20-30% more power than winter months.
Watch for regular charging cycles in your battery system if you have one installed. A healthy battery should maintain 80-100% capacity during sunny days and shouldn’t drop below 20% charge during normal use. Your system should automatically switch between solar, battery, and grid power without any noticeable interruption to your home’s power supply.
Warning Signs and Alerts
Being proactive in monitoring your solar system can prevent major issues and ensure optimal performance. Keep an eye out for these key warning signs that may indicate your system needs attention:
A sudden drop in energy production is one of the most common red flags. If you notice your system generating significantly less power than usual during similar weather conditions, this could indicate panel damage or inverter issues.
Check your monitoring app or display regularly for error messages or unusual readings. Red indicator lights on your inverter, or frequent system shutdowns, warrant immediate attention from a qualified technician.
Watch for physical signs of wear on your panels, such as discoloration, cracks, or debris accumulation. After storms, inspect for any visible damage or loose connections. Excessive heat around the inverter or unusual noises like buzzing or clicking should also prompt investigation.
Your electricity bills can also signal problems. If you notice unexpectedly high charges despite similar usage patterns, your system might not be performing at its best.
Many modern solar systems include smart monitoring features that send automatic alerts to your phone or email when issues arise. Make sure these notifications are enabled and properly configured.
Remember that addressing minor issues promptly can prevent more costly repairs down the line and help maintain your system’s efficiency for years to come.
Maintaining a proactive approach to monitoring and system maintenance is crucial for maximizing the benefits of your residential solar installation. By regularly checking system performance through monitoring apps and conducting visual inspections, you can ensure your solar investment continues to deliver optimal returns for years to come.
Regular monitoring helps you quickly identify any drops in energy production, allowing you to address issues before they become major problems. This proactive stance not only protects your investment but also ensures consistent energy savings throughout the system’s lifetime. Many homeowners report that their monitoring habits have helped them save hundreds of dollars by catching and resolving minor issues early.
Modern solar monitoring systems make it easier than ever to track your system’s performance. Through user-friendly apps and online portals, you can view real-time energy production data, compare historical performance, and receive instant notifications if something requires attention. This level of insight helps you understand your system’s behavior and make informed decisions about energy usage.
Remember that a well-maintained solar system typically performs 20-30% better than a neglected one. By implementing regular cleaning schedules, checking connections, and monitoring performance metrics, you’re not just protecting your investment – you’re ensuring maximum environmental impact and financial returns. Make monitoring and maintenance part of your regular routine, and you’ll enjoy reliable, efficient solar power for decades to come.
The small effort required for regular monitoring pays significant dividends in system longevity, performance, and peace of mind. Your solar system is a long-term investment in sustainable living, and proper attention to its care will ensure it continues to serve your home effectively.









