Harness the power of series-parallel solar panel configurations to maximize your home’s energy production while ensuring system reliability. By connecting four solar panels in a series-parallel arrangement, you create a balanced electrical circuit that combines the voltage benefits of series wiring with the current advantages of parallel connections. This versatile setup delivers optimal performance during partial shading conditions and provides greater flexibility for system maintenance. Understanding this configuration is crucial for homeowners seeking to optimize their solar investment, as it offers improved efficiency and reduced vulnerability to individual panel failures compared to purely series or parallel arrangements. Whether you’re upgrading an existing system or planning a new installation, mastering the series-parallel connection of four solar panels unlocks the perfect balance between power output and system resilience.
Understanding Series-Parallel Solar Panel Configurations
Series vs. Parallel: The Key Differences
When designing a solar panel system, understanding the difference between series and parallel connections is crucial. In a series connection, solar panels are linked end-to-end, like a chain, which adds up their voltages while maintaining the same current. This configuration can help achieve the maximum voltage of solar panels needed for your inverter to operate efficiently.
Parallel connections, on the other hand, link panels side by side, combining their currents while keeping voltage constant. Think of it like multiple lanes on a highway – more lanes mean more traffic flow, just as parallel connections allow more current to flow through the system.
The key distinction lies in their electrical behavior: series connections increase voltage, while parallel connections increase current. This difference matters because your choice affects how your system performs under various conditions. Series connections might struggle if one panel is shaded, while parallel connections can maintain better performance when partially obstructed. Understanding these differences helps you make informed decisions about your solar panel configuration and maximize your system’s energy production.
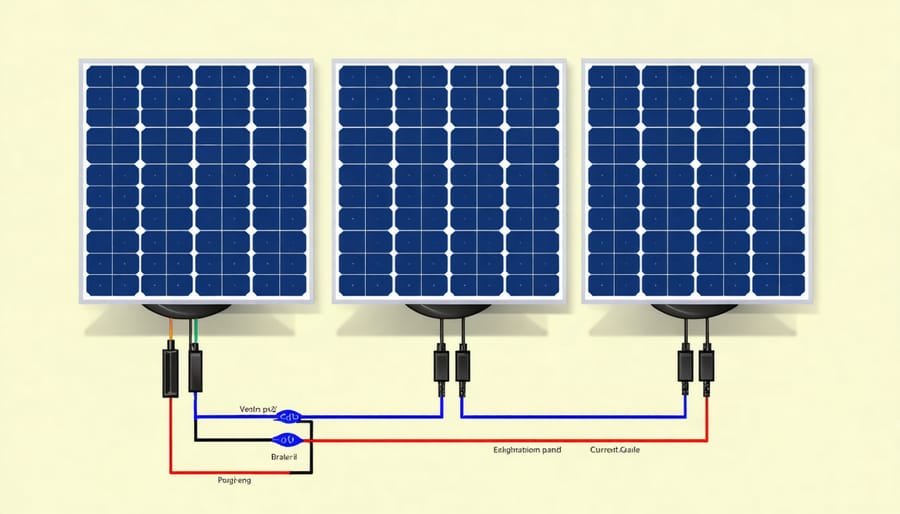
Why Choose Series-Parallel Configuration
A series-parallel configuration with four solar panels offers the perfect balance of voltage and current for most home solar setups. This arrangement combines the best of both worlds – the higher voltage benefits of series wiring with the reliability advantages of parallel connections. By splitting your four panels into two parallel strings of two series-connected panels, you create a more resilient system that continues producing power even if one panel is partially shaded or malfunctioning.
This setup also provides greater flexibility in system design and future expansion. You’ll achieve optimal power output while maintaining safer voltage levels compared to a pure series configuration. The balanced current flow helps extend your system’s lifespan by reducing strain on individual components, and the configuration makes maintenance simpler since you can isolate and troubleshoot specific strings independently.
For homeowners, this arrangement typically results in more consistent power production throughout the day and better overall system efficiency. It’s particularly effective in areas with varying sunlight conditions or partial shade, making it an ideal choice for residential installations where reliability and performance are top priorities.
Diagnosing Common Issues in Series-Parallel Systems
Voltage Drop Detection
Regular voltage checks are essential for maintaining your series-parallel solar panel system’s efficiency. Using a digital multimeter, you can easily measure voltage drops across your array to ensure optimal performance. Start by testing each panel individually during peak sunlight hours, noting the readings for comparison. A properly functioning panel should produce voltage close to its rated specifications.
When troubleshooting solar panel wiring problems, pay special attention to voltage differences between parallel strings. In a healthy system, parallel strings should show nearly identical voltage readings. If you notice a significant difference (more than 1-2 volts), this could indicate an issue with one of the panels or connections.
Common signs of voltage drop issues include:
– Unexpectedly low power output
– Inconsistent readings between parallel strings
– Sudden drops in system performance
– Warm connection points
To check for voltage drops, measure:
– Individual panel output
– Combined string voltage
– Total system voltage at the inverter input
– Connection points between panels
If you detect unusual voltage readings, inspect all connections for corrosion, loose wires, or damage. Clean connections and tighten any loose components. For persistent issues, consider consulting a solar professional to prevent potential system damage and ensure safe operation.

Current Imbalance Testing
Testing your solar panel array for current imbalances is essential for maintaining optimal performance. A simple way to check for imbalances is to measure the current output of each panel individually using a multimeter. In a properly functioning series-parallel configuration, panels in the same string should produce similar current readings under identical conditions.
Start by checking each panel’s current output during peak sunlight hours. If you notice significant differences between panels in the same string (more than 10% variation), this could indicate a problem. Common causes include partial shading, dirt accumulation, or panel degradation.
To conduct a thorough test, monitor your system’s performance throughout the day. Keep a log of readings and look for patterns. Pay special attention to early morning and late afternoon measurements, as these times often reveal shading issues that might not be apparent at midday.
If you discover imbalances, first check for obvious issues like debris or shade. Clean your panels if necessary and trim any overhanging branches. For persistent problems, inspect the wiring connections and bypass diodes. Sometimes, simply tightening loose connections can resolve current flow issues.
Remember that some variation is normal, especially in changing weather conditions. However, consistent significant differences warrant professional inspection to prevent reduced system efficiency and potential damage to your solar array.
Advanced Testing Tools and Techniques

Essential Testing Equipment
To properly test and maintain your 4-panel series-parallel solar setup, you’ll need several essential tools. A quality digital multimeter is your most important piece of equipment, allowing you to measure voltage, current, and resistance across your system. Look for one with DC voltage measurement capabilities of at least 600V and current measurement up to 10A.
A solar irradiance meter helps you verify if your panels are receiving adequate sunlight and performing as expected. While professional models can be expensive, affordable handheld versions work well for home use. An infrared thermometer is invaluable for detecting hot spots or unusual temperature variations that might indicate panel issues.
Keep basic safety equipment on hand, including insulated gloves rated for electrical work and safety glasses. A battery hydrometer is essential if you’re using lead-acid batteries in your system. For detailed performance tracking, consider investing in a simple data logger that can record voltage and current readings over time.
Don’t forget basic hand tools like wire strippers, crimpers, and an assortment of screwdrivers for maintenance and minor repairs. Having these tools ready ensures you can quickly diagnose issues and keep your solar system running efficiently.
Step-by-Step Testing Process
To ensure your series-parallel solar panel setup is working correctly, follow these simple diagnostic steps:
Start by measuring the voltage output of each individual panel using a multimeter set to DC voltage mode. Record these readings when panels are disconnected from the system. Ideally, each panel should show similar voltage readings in full sunlight.
Next, check the series connections by measuring voltage across each pair of panels. The reading should roughly equal the sum of individual panel voltages. For example, if each panel produces 24V, paired panels should show around 48V.
Then, verify the parallel connection between the two series strings. The voltage should match a single series pair, while the current capacity doubles. Use your multimeter’s DC current setting for this test.
Look for these common issues:
– Significantly different voltage readings between panels
– Loose or corroded connections
– Damaged wiring insulation
– Dust or debris covering panels
If readings don’t match expected values, inspect all connection points and clean panel surfaces. For persistent problems, consider having a professional solar technician perform a detailed diagnostic check.
Remember to perform these tests during peak sunlight hours for the most accurate results.
Maximizing System Performance
To maximize your solar system performance in a series-parallel configuration, regular maintenance and smart monitoring are essential. Start by keeping your panels clean and free from debris, as even small shadows can affect the entire string’s output. Check the mounting hardware quarterly to ensure all panels remain properly aligned and secure.
Monitor voltage levels across each string using a multimeter during peak sunlight hours. Ideally, parallel strings should show similar voltage readings – significant differences might indicate a problem requiring attention. Install microinverters or power optimizers on each panel to minimize the impact of shading and ensure each panel operates at its peak potential.
Regularly inspect wire connections and junction boxes for signs of wear or corrosion. Loose connections can create resistance, reducing overall system efficiency. Consider adding a monitoring system that tracks individual panel performance, helping you quickly identify and address any issues before they impact your entire array.
During winter months, clear snow promptly to prevent extended power loss. Trim nearby trees or vegetation that might cast shadows on your panels as the seasons change. Schedule professional inspections annually to verify proper functioning of all system components and catch potential problems early.
Remember that proper initial installation is crucial – ensure panels are oriented optimally and strings are balanced for your specific location and energy needs.
Understanding and maintaining a 4-panel series-parallel configuration doesn’t have to be complicated. By following proper diagnostic procedures and regular maintenance checks, you can ensure your solar system operates at peak efficiency. Remember that voltage measurements across parallel strings should be equal, while current readings in series connections should match. Regular monitoring of these values helps catch potential issues early, saving you time and money in the long run. If you notice any inconsistencies, don’t hesitate to consult with a qualified solar professional. With proper care and attention, your series-parallel solar array will continue to provide reliable, clean energy for your home while maximizing your investment in sustainable power generation.









