Transform your home into a resilient power fortress by installing a reliable emergency solar system. Modern solar backup solutions offer uninterrupted power when the grid fails, letting you confidently prepare for power outages while reducing energy costs. A well-designed home solar backup system combines high-capacity batteries, efficient panels, and smart inverters to power essential appliances during emergencies – from refrigerators and medical devices to communication systems and lighting.
Unlike traditional generators, solar backup systems operate silently, require minimal maintenance, and produce clean energy year-round. They seamlessly integrate with existing home electrical systems, automatically engaging when grid power fails. By harnessing renewable energy, these systems not only provide crucial emergency power but also contribute to lower utility bills and reduced carbon emissions during normal operation.
Whether facing severe weather events, grid instability, or other emergencies, a properly sized solar backup system ensures your home remains powered and functional when you need it most. The technology has become increasingly affordable and efficient, making it an intelligent investment in both emergency preparedness and sustainable living.
Why Solar Backup Power Makes Sense

Silent Operation & Clean Energy
One of the most appealing aspects of home solar power systems is their whisper-quiet operation. Unlike traditional gas generators that produce constant noise and exhaust fumes, solar systems work silently, making them perfect for residential areas where noise regulations and neighborly consideration are important. The only sound you might hear is a slight hum from the inverter, which is typically no louder than a modern refrigerator.
Beyond the peace and quiet, solar emergency power systems offer the satisfaction of using clean, renewable energy. Every kilowatt-hour generated by your solar system reduces your carbon footprint and decreases dependence on fossil fuels. During emergencies, you can power your essential appliances without contributing to air pollution or greenhouse gas emissions.
This environmentally friendly approach also means no fuel storage concerns, no complicated maintenance schedules, and no worries about fuel availability during prolonged power outages. The sun provides free, unlimited energy during daylight hours, while your battery system stores power for nighttime use, creating a sustainable and reliable emergency power solution.
Low Maintenance & Fuel Independence
One of the most appealing aspects of solar emergency power systems is their minimal maintenance requirements and freedom from fuel dependencies. Unlike traditional generators that need regular fuel purchases, storage, and maintenance, solar systems operate purely on sunlight – a free and abundant resource. There’s no need to worry about storing volatile fuels or making emergency trips to the gas station during power outages.
Solar panels typically only require occasional cleaning to remove dust and debris, which can be done with water and a soft brush. Most quality systems can operate effectively for 25-30 years with virtually no moving parts to maintain or replace. The batteries, while requiring eventual replacement, typically last 10-15 years with proper care.
This low-maintenance nature makes solar systems particularly reliable during extended emergencies when access to fuel or repair services might be limited. You’ll also avoid the hassles of fuel storage, such as rotation schedules, spillage risks, and storage space requirements. For homeowners seeking a truly hands-off backup power solution, solar systems offer unmatched convenience and peace of mind.
Essential Components of a Home Solar Emergency System
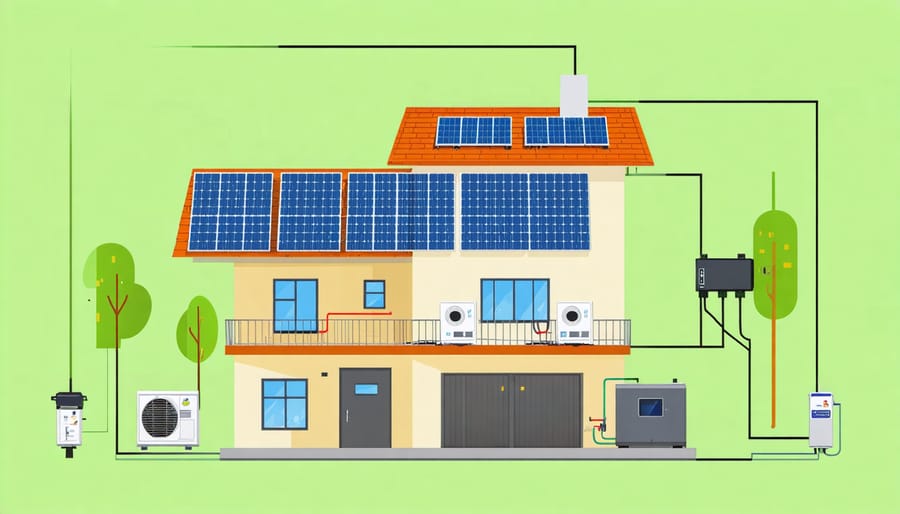
Solar Panels & Mounting
For a home emergency solar power system, you’ll typically need 4-6 solar panels rated between 200-400 watts each to provide adequate backup power for essential appliances. When selecting panels, focus on monocrystalline or polycrystalline options, as these offer the best balance of efficiency and cost for residential use.
Mounting location is crucial for optimal performance. South-facing roof installations generally capture the most sunlight throughout the day, though east or west-facing positions can still be effective. Ensure your roof can support the additional weight, which averages 40-50 pounds per panel including mounting hardware.
Ground mounting is an excellent alternative if roof installation isn’t feasible. This option makes maintenance easier and allows for optimal angle adjustment, though it requires more yard space and additional security considerations.
For emergency systems, consider portable panel options that can be stored and deployed as needed. These typically offer less power but provide flexibility during extended outages or evacuation scenarios. Whatever mounting solution you choose, ensure it meets local wind resistance requirements and building codes.
Battery Storage Solutions
When it comes to storing solar energy for emergency use, choosing the right battery system is crucial. Lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries are the two main options for home solar storage. While lead-acid batteries are more budget-friendly, lithium-ion batteries offer better efficiency, longer lifespan, and require less maintenance.
To determine your battery storage needs, start by listing your essential appliances and their power requirements. A typical emergency backup system should support your refrigerator, lighting, communication devices, and basic medical equipment. Most homeowners find that a 10-15 kWh battery system provides adequate backup power for 24-48 hours of essential use.
Lithium-ion batteries, particularly LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries, have become increasingly popular due to their safety features and impressive 10-15 year lifespan. These batteries can be discharged up to 80% without damage, compared to only 50% for lead-acid batteries, giving you more usable capacity.
Consider installing a modular battery system that allows you to add capacity over time. This approach lets you start with a basic setup and expand as your needs or budget grow. Most modern battery systems also include smart monitoring capabilities, helping you track power usage and battery health through your smartphone.
For maximum reliability, place your batteries in a temperature-controlled, ventilated space, and implement proper maintenance schedules according to manufacturer guidelines.
Inverters & Control Systems
Inverters are the heart of your emergency solar power system, converting DC power from your solar panels and batteries into usable AC power for your home. Modern inverters come in two main types: string inverters for whole-house systems and microinverters that operate individually on each panel. For emergency backup systems, hybrid inverters are particularly valuable as they can seamlessly switch between grid and battery power.
The control system acts as your system’s brain, monitoring power generation, consumption, and storage. Smart controllers allow you to protect your solar investment by automatically managing power flow and preventing system overload. Many modern systems include user-friendly apps that let you track performance and adjust settings from your smartphone.
When selecting these components, focus on reliability and compatibility with your specific setup. Look for inverters with high efficiency ratings (95% or better) and control systems with automatic shutdown features for safety. While premium components may cost more initially, they typically offer better long-term performance and peace of mind during emergencies.
Sizing Your Emergency Solar System
Critical Load Assessment
Determining your emergency power needs starts with identifying your critical loads – the essential devices and appliances you’ll need during a power outage. Begin by making a list of must-have items like refrigeration, lighting, medical equipment, and communication devices.
To calculate your power requirements, check the wattage rating on each device. This information is usually found on a label or in the user manual. For appliances that list amps instead of watts, multiply the amps by the voltage (typically 120V) to find the wattage.
Create a simple spreadsheet with three columns: device name, wattage, and daily hours of use. Multiply each device’s wattage by its hours of use to determine daily watt-hours. Add up all your daily watt-hours to find your total power requirement.
Remember to account for surge power – the extra electricity needed when devices first start up. Refrigerators and air conditioners, for example, can require 3-7 times their running wattage during startup.
A typical emergency backup system for essential loads might need to support:
– Refrigerator: 150-200 watts
– LED lighting: 5-10 watts per bulb
– Phone chargers: 5-10 watts
– Wi-Fi router: 10-20 watts
– Medical equipment: varies
Always add a 20% buffer to your calculations to ensure your system can handle unexpected needs during emergencies.
Storage Capacity Planning
Planning your battery storage capacity is crucial for ensuring your emergency solar power system meets your needs during outages. Start by listing your essential appliances and their power consumption in watts. Common must-haves include refrigerators, lighting, medical equipment, and communication devices.
To calculate your daily energy needs, multiply each appliance’s wattage by the hours you’ll use it per day. For example, a 100-watt refrigerator running 24 hours uses 2,400 watt-hours daily. Add up all your appliances’ daily usage to determine your total energy requirement.
Consider how long you want your backup power to last. For short outages, a day or two of backup might suffice. However, for areas prone to extended power losses, aim for 3-7 days of capacity. Remember to factor in weather conditions – cloudy days reduce solar charging efficiency.
Most home backup systems use lithium-ion batteries, which typically come in 10-15 kilowatt-hour capacities. For a typical household running essential appliances, plan for at least 20-30 kilowatt-hours of storage to maintain power for 2-3 days. Include a 20% buffer in your calculations to account for battery efficiency losses and unexpected power needs.
Don’t forget to consider future needs. If you’re planning to add more appliances or anticipate increased power requirements, it’s wise to install additional capacity during initial setup rather than upgrading later.
Installation & Maintenance
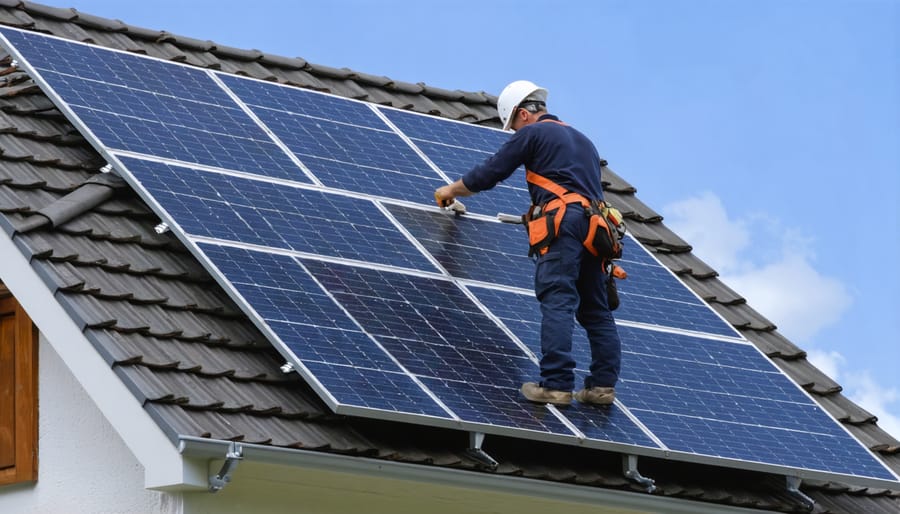

Professional vs DIY Installation
When it comes to installing a home emergency solar power system, you have two main options: professional installation or doing it yourself. Professional installation offers several advantages, including guaranteed compliance with local building codes, proper system sizing, and expert workmanship. Certified installers bring years of experience and can typically complete the installation in 1-2 days, plus they often provide warranties covering both the equipment and their work.
However, professional installation can add significantly to your overall costs, sometimes increasing the total project budget by 30-50%. For those with technical skills and DIY experience, self-installation can be a viable money-saving option, especially for smaller emergency systems that don’t require complex roof mounting or electrical work.
If you choose the DIY route, you’ll need to research local permit requirements, understand basic electrical concepts, and carefully follow manufacturer installation guides. Ground-mounted systems and portable solar generators are typically easier for DIY installation compared to roof-mounted arrays. Keep in mind that some equipment warranties may be void if not installed by certified professionals.
Consider your technical abilities, budget, and system complexity when making your choice. While DIY installation can save money, the peace of mind and guaranteed results from professional installation might be worth the extra investment, especially for larger or more complex systems.
Maintenance Schedule & Tips
Regular maintenance of your emergency solar power system is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Every three months, take time to maintain your solar panels by cleaning them with water and a soft brush to remove dust, leaves, and debris. This simple task can improve efficiency by up to 5%.
Inspect your battery bank monthly, checking for corrosion, loose connections, or unusual swelling. Keep battery terminals clean and tight, and ensure proper ventilation in the battery storage area. Test your backup system quarterly by simulating a power outage to verify all components work correctly.
Install protective measures to prevent bird-related issues and protect against environmental damage. Check weather seals and mounting hardware annually to ensure everything remains secure and watertight.
Monitor your system’s performance through its display panel or app regularly. Keep a maintenance log to track cleaning dates, battery replacements, and system checks. Replace batteries according to manufacturer recommendations, typically every 5-10 years depending on the type.
Store basic cleaning supplies and tools nearby for quick maintenance. Consider scheduling professional inspections annually to catch potential issues early and ensure your system remains ready for emergencies.
Investing in a home emergency solar power system is more than just a backup plan – it’s a step toward energy independence and environmental responsibility. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored the essential components, sizing considerations, and practical steps needed to create a reliable solar emergency power solution for your home.
Remember that a well-designed emergency solar system can provide peace of mind during power outages while contributing to your home’s overall energy efficiency and sustainability. By combining solar panels, batteries, and proper installation, you can create a robust backup power solution that serves your family when they need it most.
Start your journey toward solar emergency preparedness by assessing your power needs and consulting with qualified solar professionals. Consider starting small with basic backup capabilities and expanding your system over time as your needs and budget allow. The initial investment in solar emergency power can lead to long-term savings while ensuring your home remains powered during grid failures.
Take action today by conducting a home energy audit and researching local solar installers. With proper planning and implementation, your emergency solar power system can become an integral part of your home’s resilience strategy, providing reliable backup power while reducing your carbon footprint and energy costs.
The path to energy independence starts with a single step – make yours count by beginning your solar emergency preparedness journey today.









