Understanding solar panel output is crucial for making smart energy decisions. A typical solar panel generates between 1.3 to 1.6 kilowatt-hours (kWh) per square foot annually, though actual production varies significantly based on location, installation angle, and environmental conditions. This efficiency translates to approximately 15-18 watts per square foot under ideal conditions.
For homeowners considering solar installation, these numbers mean a 100-square-foot array could generate 130-160 kWh annually in optimal conditions. Modern residential solar panels are becoming increasingly efficient, with some premium models now achieving conversion rates above 20%, maximizing energy production in limited space.
Factors like geographic location, roof orientation, shade patterns, and local weather patterns can impact these baseline figures by 20-30%. Understanding your specific situation helps set realistic expectations for solar production and ensures your investment delivers the expected returns. Professional solar assessments can provide precise calculations tailored to your property’s unique characteristics.
Understanding kWh Per Square Foot Basics
What These Numbers Mean for Your Home
To put these numbers into perspective for your home, consider that an average American household uses about 30 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity daily. Understanding your solar system size requirements starts with your monthly energy consumption and available roof space.
For example, if your panels produce 2 kWh per square foot annually, and your home uses 900 kWh monthly, you’d need roughly 450 square feet of solar panels to meet your yearly energy needs. This typically translates to about 25-30 panels for a complete home system.
Keep in mind that most homes don’t need to generate 100% of their energy from solar panels. Even covering 70-80% of your energy needs can significantly reduce your utility bills while maintaining a practical system size. Many homeowners start with a smaller system and expand it later as their needs change or budget allows.
Remember that these calculations are estimates, and your actual needs may vary based on local weather patterns, roof orientation, and energy consumption habits.
Average Output Expectations
In typical residential installations, solar panels generally produce between 1.3 to 1.6 kilowatt-hours (kWh) per square foot annually, though this can vary based on location and conditions. For perspective, a 100-square-foot solar array might generate between 130 to 160 kWh per year in moderate sunlight conditions.
Premium solar panels can achieve higher outputs, reaching up to 2 kWh per square foot annually in optimal conditions. However, most homeowners can expect their systems to perform within the standard range. A typical 6-kilowatt residential system, covering approximately 300-400 square feet, usually generates between 400-600 kWh per month, or 4,800-7,200 kWh annually.
These figures translate to real-world savings – a properly sized system can offset 60-90% of a typical home’s electricity needs. Keep in mind that first-year production is usually the highest, with a small decrease (about 0.5-1%) in efficiency each subsequent year. Modern panels are designed to maintain at least 80% of their initial output capacity even after 25 years of service.
Factors Affecting Your Panel’s Output
Geographic Location and Sun Exposure
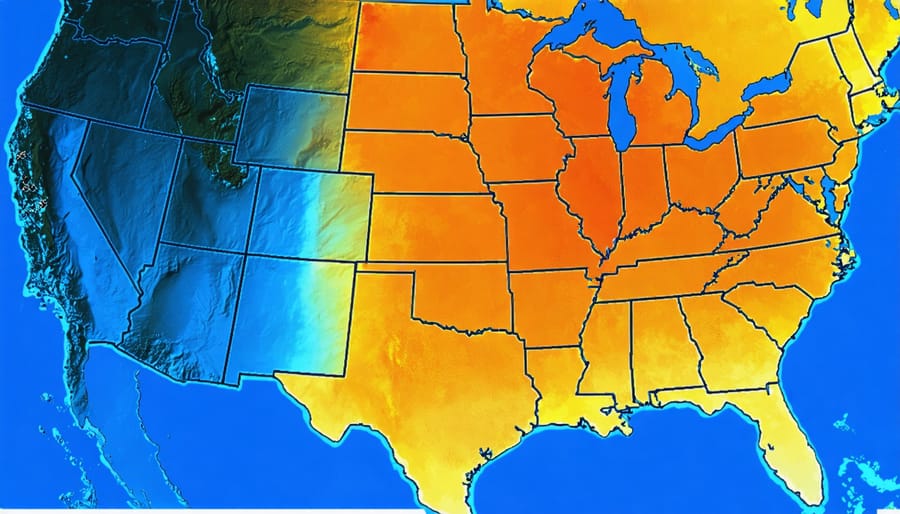
Your solar panels’ power generation depends heavily on where you live and how much sunlight your location receives throughout the year. Southern states like Arizona and California typically generate more solar energy than northern regions due to greater sun exposure and clearer skies. For example, a solar panel in Phoenix might produce 30% more energy than the same panel installed in Seattle.
The position of your roof and its exposure to sunlight also plays a crucial role. South-facing roofs in the Northern Hemisphere typically receive the most direct sunlight, making them ideal for solar panel installation. A roof angle between 30-45 degrees usually provides optimal sun exposure throughout the year.
Local weather patterns affect your panels’ performance too. Areas with frequent cloud cover or rain will see lower energy production compared to sunny regions. However, modern solar panels can still generate significant power even in cloudy conditions – they just work at reduced efficiency.
To maximize your solar investment, consider local solar irradiance maps and consult with installers who understand your area’s specific conditions. They can help position your panels for optimal sun exposure and estimate realistic power generation expectations.
Panel Quality and Technology
The quality and technology of your solar panels significantly impact their power output per square foot. Today’s most efficient solar panels can convert up to 23% of sunlight into electricity, compared to budget panels that typically achieve 15-17% efficiency.
Premium panels often use monocrystalline silicon cells, which pack more power-generating capacity into a smaller space. These high-end panels can produce 18-22 watts per square foot under ideal conditions, while standard polycrystalline panels typically generate 15-17 watts per square foot.
Manufacturing quality also plays a crucial role in long-term performance. Well-made panels maintain their efficiency better over time, with premium brands guaranteeing at least 85% of their original output after 25 years. Lower-quality panels may degrade more quickly, potentially losing up to 20% of their efficiency within the first decade.
When choosing panels, consider that higher upfront costs for quality technology often translate to better long-term value through increased energy production and reliability.
Installation Angle and Positioning
The angle and position of your solar panels play a crucial role in maximizing their power output. In North America, south-facing panels typically generate the most electricity, with an ideal tilt angle between 30-45 degrees, depending on your latitude. While flat installations are possible, they can collect dust and debris more easily, reducing efficiency by up to 10%.
For optimal performance, ensure your panels aren’t shaded by nearby trees, buildings, or other obstacles during peak sunlight hours (10 AM to 2 PM). Every hour of direct shade can reduce daily output by 5-10%. Consider seasonal sun patterns too – a slightly steeper angle works better in winter, while a flatter position captures more summer sunshine.
Professional installers can calculate the perfect angle for your specific location, ensuring you get the most kWh per square foot possible from your investment.
Maximizing Your Solar Investment
Space-Efficient Panel Selection
When choosing solar panels for your home, maximizing power output within your available space is crucial. High-efficiency panels, typically ranging from 19% to 23% efficiency, can generate more power per square foot than standard panels. For example, a premium panel might produce 19-21 watts per square foot, while a standard panel might only generate 15-17 watts in the same space.
Look for panels with higher power density ratings, which indicate how much power they can produce relative to their physical size. Modern monocrystalline panels often offer the best space efficiency, making them ideal for homes with limited roof area. Some top-tier panels can now produce up to 400-450 watts in roughly the same dimensions as older 250-watt models.
Consider these practical tips for space-efficient panel selection:
– Compare power ratings (watts) rather than just panel size
– Calculate the watts per square foot for each panel you’re considering
– Factor in your roof’s shape and orientation
– Account for required spacing between panels for maintenance
– Consider bifacial panels for increased output in the same footprint
Remember that the most expensive panels aren’t always the most space-efficient choice. Focus on finding the sweet spot between cost, available space, and power output. Many homeowners find that mid-tier panels with good efficiency ratings offer the best value while making effective use of limited roof space.
Maintenance for Peak Performance
Regular maintenance is key to ensuring your solar panels continue delivering optimal power output. To boost your solar panel performance, follow these simple yet effective maintenance practices.
Clean your panels every 3-4 months using plain water and a soft brush or sponge. Avoid harsh chemicals that might damage the protective glass surface. If you live in a dusty area or near trees, you may need to clean more frequently to prevent debris buildup that can reduce efficiency.
Regularly inspect for any physical damage, loose connections, or shading issues from growing vegetation. Trim nearby trees or bushes that cast shadows on your panels, as even partial shade can significantly impact power generation.
Monitor your system’s output through its monitoring app or display. If you notice unexpected drops in production, schedule a professional inspection. Most manufacturers recommend an annual professional check-up to ensure all components are functioning correctly and safely.
During winter, clear snow accumulation promptly but safely. Consider installing a monitoring system if you haven’t already – it helps detect performance issues early and maximizes your energy savings.
Future-Proofing Your System
To ensure your solar panel system remains efficient and valuable for years to come, consider implementing a few forward-thinking strategies. Start by choosing high-quality panels with proven longevity and degradation rates below 0.5% per year. Many premium panels now come with 25-30 year warranties, offering long-term peace of mind.
Install a smart monitoring system to track your panels’ performance and detect efficiency drops early. Modern monitoring solutions can alert you to potential issues before they significantly impact your energy production, helping maintain optimal kWh output per square foot over time.
Consider leaving room for future expansion when planning your initial installation. This might mean installing extra inverter capacity or ensuring your roof has additional suitable space for more panels. As battery technology continues to improve, you may want to add energy storage to your system later.
Regular maintenance and cleaning schedules will help maintain peak efficiency. Additionally, investing in micro-inverters or power optimizers can make your system more adaptable to future technological improvements while minimizing the impact of partial shading or panel degradation.
Understanding solar panel efficiency and power output is crucial for making an informed decision about your renewable energy investment. While the average solar panel generates between 1.3 to 2 kWh per square foot annually, remember that your specific results will depend on various factors including location, panel orientation, and local weather patterns.
By optimizing your solar installation through proper positioning, regular maintenance, and selecting high-efficiency panels, you can maximize your energy production and financial returns. Modern solar technology continues to advance, offering increasingly efficient solutions for homeowners looking to reduce their carbon footprint and energy bills.
Taking the step toward solar energy isn’t just about immediate savings – it’s an investment in a sustainable future. With federal tax incentives, decreasing installation costs, and improving technology, there’s never been a better time to consider solar power for your home. By understanding the basics of solar panel output and efficiency, you’re well-equipped to make an informed decision about your home’s energy future.
Start by getting a professional assessment of your property’s solar potential and explore the options available in your area. The path to clean, renewable energy begins with taking that first step.