Resilient solar solutions represent more than just energy independence – they’re a critical investment in your home’s future security and sustainability. As extreme weather events become more frequent and power grids face mounting pressures, homeowners need solar systems that deliver reliable performance through any challenge. Modern resilient solar installations combine robust hardware, intelligent system design, and advanced energy storage to create a power solution that works when you need it most.
The key to true solar resilience lies in thoughtful system integration. By pairing high-efficiency panels with battery storage, sophisticated monitoring technology, and professional installation, homeowners can create an energy ecosystem that maintains power during outages, optimizes daily performance, and adapts to changing conditions. These systems not only protect against disruption but also deliver consistent savings while increasing property value.
Whether you’re considering your first solar installation or upgrading an existing system, understanding the components of resilient solar design is essential for making informed decisions that will serve your home for decades to come. From panel selection and mounting systems to backup power solutions and maintenance protocols, each element plays a vital role in creating a truly dependable clean energy solution.
Core Components of a Resilient Solar System
High-Quality Panels Built for Extreme Weather
Modern weather-resistant solar solutions are engineered to withstand nature’s toughest challenges. Today’s premium solar panels undergo rigorous testing to ensure they can handle extreme temperatures, heavy snow loads, and hurricane-force winds up to 140 mph.
These panels feature reinforced frames made from anodized aluminum, which resist corrosion and maintain structural integrity in harsh conditions. The tempered glass covering is typically 3.2mm thick and treated with anti-reflective coating, allowing it to withstand hail impacts while maximizing energy absorption.
Most quality panels are rated for temperature variations from -40°F to 185°F, ensuring reliable performance year-round. They’re also certified to handle snow loads of up to 5,400 Pascal (Pa) and wind loads of 2,400 Pa. This means your solar investment stays protected even during severe weather events.
Many manufacturers now include advanced water-sealing technology and micro-crack prevention features, extending panel life well beyond their 25-year warranty period. These innovations mean homeowners can count on consistent energy production regardless of weather conditions.

Advanced Battery Storage Solutions
Modern battery storage systems are the backbone of truly resilient solar solutions, providing reliable power even when the sun isn’t shining. Today’s lithium-ion batteries offer exceptional performance and longevity, storing excess solar energy during peak production hours for use during nighttime or cloudy periods.
These advanced systems come with smart monitoring capabilities, allowing homeowners to track energy usage and storage levels through user-friendly mobile apps. When paired with solar panels, batteries can provide complete energy independence during grid outages, keeping essential appliances running for days.
Most home battery systems range from 10 to 15 kilowatt-hours of storage capacity, enough to power an average home’s critical loads for 24-48 hours. Some homeowners choose to install multiple batteries for extended backup capability. The latest models feature improved depth of discharge, meaning you can use more of the stored energy without damaging the battery.
Beyond emergency backup, these systems help maximize solar investment by storing excess energy instead of sending it back to the grid, particularly beneficial in areas without favorable net metering policies.
Smart Monitoring Systems
Modern solar installations come equipped with smart monitoring systems that act like a health tracker for your solar setup. These systems provide real-time data about your system’s performance, energy production, and potential issues through user-friendly mobile apps or web portals. You’ll receive instant alerts if production drops unexpectedly or if maintenance is needed, helping you catch and address problems before they impact your energy supply. Many monitoring systems also track weather patterns and automatically adjust system settings for optimal performance. This proactive approach not only extends your system’s lifespan but also ensures you’re getting the most from your solar investment. The best part? You can check your system’s performance and energy savings from anywhere, giving you complete control and peace of mind.
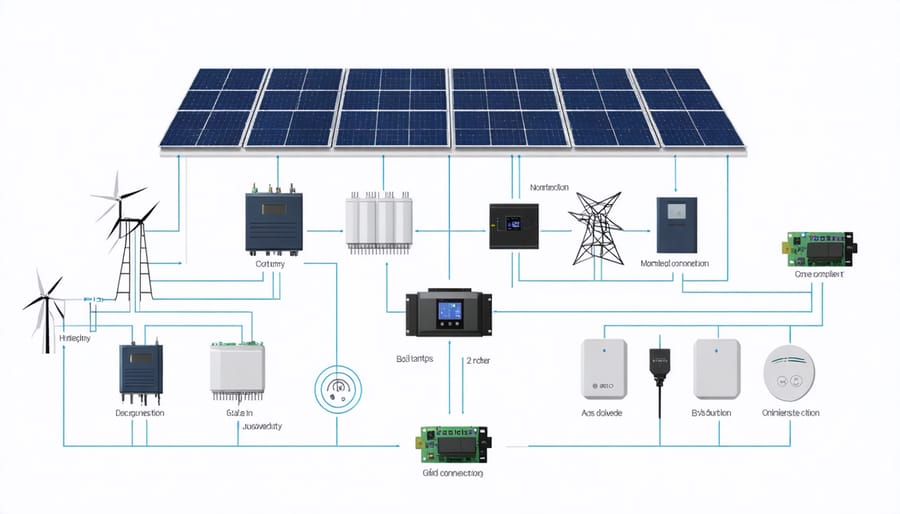
Smart Design Strategies for Maximum Reliability
Optimal Panel Placement and Mounting
Proper panel placement and mounting are crucial factors in creating a resilient solar system that stands the test of time. Start by assessing your roof’s orientation – south-facing surfaces in the Northern Hemisphere typically receive optimal sunlight exposure. Aim for a roof angle between 30-45 degrees to maximize energy production while allowing natural cleaning from rainfall.
When mounting panels, consider your local climate conditions. In areas with heavy snowfall, install panels at a steeper angle to encourage snow sliding off. For regions prone to high winds, use additional mounting points and reinforced racking systems rated for your area’s maximum wind speeds.
Leave adequate space between your roof and panels (about 4-6 inches) to allow proper airflow, which helps prevent heat buildup and maintains panel efficiency. This gap also makes maintenance easier and provides a habitat buffer for wildlife.
Choose mounting hardware made from corrosion-resistant materials like aluminum or stainless steel. All mounting points should include weatherproof flashing to prevent water infiltration, and use appropriate sealants rated for outdoor use. Double-check that your roof can support the additional weight of the solar system, including snow loads in winter.
For ground-mounted systems, ensure foundations extend below the frost line and use concrete footings to prevent shifting. Regular inspection of mounting hardware and tightening of any loose components will help maintain system integrity over time.
Redundancy Planning
A well-designed solar system needs multiple layers of protection to ensure continuous power supply. Start by installing a hybrid inverter that can work with both solar panels and battery storage, allowing seamless switching between power sources. Include at least two batteries in your setup – one primary and one backup – to maintain power during extended periods of low sunlight or grid outages.
Consider incorporating micro-inverters or power optimizers for each panel, rather than relying on a single string inverter. This ensures that if one panel fails, the others continue operating at full capacity. Adding a backup generator can provide an additional safety net during extreme weather events or prolonged power outages.
Smart monitoring systems help track system performance and alert you to potential issues before they become critical. Install surge protectors and lightning arrestors to shield your equipment from electrical surges. For areas prone to severe weather, reinforced mounting systems and impact-resistant panels offer extra durability.
Remember to keep essential spare parts on hand, such as fuses and connectors, for quick repairs when needed. Regular maintenance checks help identify potential weaknesses before they lead to system failures.
Grid Connection vs. Independence
When considering solar power systems, homeowners often face the choice between staying connected to the utility grid or pursuing complete energy independence. Both approaches offer distinct advantages. Grid-connected systems provide reliable backup power and the ability to sell excess energy back to utilities through grid connection options, making them a practical choice for most households.
Off-grid systems, while requiring more initial investment in battery storage, offer true energy independence and protection from utility outages. Many homeowners opt for a hybrid approach, maintaining grid connection while incorporating battery backup for essential circuits. This setup provides the best of both worlds: daily solar benefits with utility backup, plus critical power security during outages.
Consider your energy needs, local climate, and budget when deciding. Grid-connected systems typically cost less upfront and offer simpler maintenance, while off-grid systems provide maximum resilience but demand more comprehensive battery storage and system monitoring. Your local utility policies and available incentives should also factor into this important decision.
Maintenance Best Practices

Regular Inspection Schedule
Regular system inspections are crucial for maintaining your solar installation’s peak performance and longevity. For optimal results, schedule comprehensive checks every six months, ideally in spring and fall when weather conditions are mild.
Your bi-annual inspection checklist should include:
1. Visual inspection of solar panels for dirt, debris, or physical damage
2. Check mounting hardware and roof attachments for tightness
3. Verify inverter operation and review performance metrics
4. Examine electrical connections and wiring
5. Clean panels if necessary
6. Review system monitoring data for any performance issues
Monthly tasks (can be done by homeowners):
– Monitor system output through your app or monitoring system
– Quick visual check for obvious issues
– Clear visible debris from panels
– Note any changes in surrounding shade conditions
Annual professional inspection should include:
– Detailed electrical testing
– Thermal imaging to detect hot spots
– Battery system health check (if applicable)
– Calibration of monitoring equipment
– Professional cleaning if needed
After severe weather events, perform additional visual inspections to ensure your system hasn’t sustained damage. Keep detailed records of all inspections and maintenance work, which can be valuable for warranty claims and system optimization. Remember, a well-maintained solar system can last well beyond its 25-year warranty period.
Emergency Preparedness
Being prepared for emergencies ensures your solar system continues providing power when you need it most. Start by creating a detailed emergency response plan that includes system shutdown procedures and emergency contact information for your solar installer and utility company.
Keep essential maintenance tools and spare parts readily available, including fuses, basic electrical tools, and cleaning supplies. Install a monitoring system that alerts you to potential issues before they become critical emergencies. This early warning system can help prevent system failures and maintain continuous power supply.
Consider installing a backup battery system to store excess energy for use during outages. Modern solar batteries can power essential appliances for several days, providing crucial support during extended power interruptions. Regularly test your backup systems, including inverters and batteries, to ensure they’re functioning correctly.
Document your system’s layout, including the location of shutdown switches, circuit breakers, and critical components. Share this information with family members so everyone knows how to safely operate the system during emergencies.
Weather-related challenges require specific preparation. Secure solar panels against high winds, clear debris regularly, and ensure proper drainage to prevent water damage. In areas prone to severe weather, consider additional mounting reinforcement and protective measures.
Remember to review and update your emergency plan annually, accounting for any system modifications or new environmental challenges. This proactive approach helps maintain system resilience and ensures reliable power generation when it matters most.
Future-Proofing Your Investment
Scalability Options
One of the best features of solar power systems is their adaptability to your changing energy needs. When planning your initial installation, consider leaving room on your roof for additional panels and ensuring your inverter can handle extra capacity. A good rule of thumb is to install an inverter that’s 20-30% larger than your current needs, making future expansions more cost-effective.
Smart panel placement is crucial for scalability. Work with your installer to create a layout that allows for seamless panel additions without disrupting your existing setup. Consider your future energy requirements, such as adding an electric vehicle charging station or a home addition, when planning your system’s growth potential.
Battery storage systems can also be scaled up over time. Starting with a smaller battery bank and expanding as needed helps manage upfront costs while maintaining the flexibility to increase storage capacity. Many modern solar systems use modular components, making it easier to add new features or upgrade existing ones without replacing the entire system.
Remember to check local regulations and ensure your electrical panel can accommodate future expansions. This forward-thinking approach helps maximize your long-term solar investment while adapting to your evolving energy needs.
Emerging Technologies
The landscape of solar resilience is rapidly evolving, with exciting innovations that promise to make solar systems even more dependable and efficient. The future of solar technology is being shaped by breakthrough developments in energy storage, with solid-state batteries offering longer lifespans and improved safety compared to traditional lithium-ion solutions.
Smart solar panels equipped with artificial intelligence are revolutionizing how systems respond to weather changes and energy demands. These intelligent panels can automatically adjust their positioning and output optimization, maximizing energy production even in challenging conditions.
Perovskite solar cells are showing promise as a more affordable and efficient alternative to traditional silicon panels, while bifacial solar panels that capture light from both sides are becoming increasingly popular for residential installations. Self-healing solar materials are also in development, which could significantly extend panel lifespan by automatically repairing minor damage from environmental exposure.
Additionally, integrated solar roof tiles and window-based solar solutions are making it easier than ever to incorporate renewable energy into your home’s design without compromising aesthetics.
As we’ve explored throughout this guide, resilient solar solutions offer homeowners a reliable path to energy independence and sustainability. By investing in quality components, implementing smart system design, and following proper maintenance protocols, you can create a solar installation that stands the test of time while delivering consistent energy savings.
Remember that resilience isn’t just about durability – it’s about creating a system that adapts to your needs and continues performing even in challenging conditions. From battery backup systems to weather-resistant mounting solutions, each element plays a crucial role in building a truly resilient solar setup.
Taking the next step toward solar resilience is easier than you might think. Start by assessing your home’s energy needs and solar potential, then connect with certified installers who can recommend appropriate system components. Consider factors like local weather patterns, roof condition, and future energy requirements when planning your installation.
Don’t forget to explore available incentives and financing options, as these can significantly reduce your initial investment. Regular maintenance and monitoring will help ensure your system’s longevity and optimal performance.
By choosing resilient solar solutions, you’re not just investing in your home’s energy future – you’re contributing to a more sustainable world while protecting yourself against rising energy costs and power outages. Take action today to begin your journey toward energy independence.









