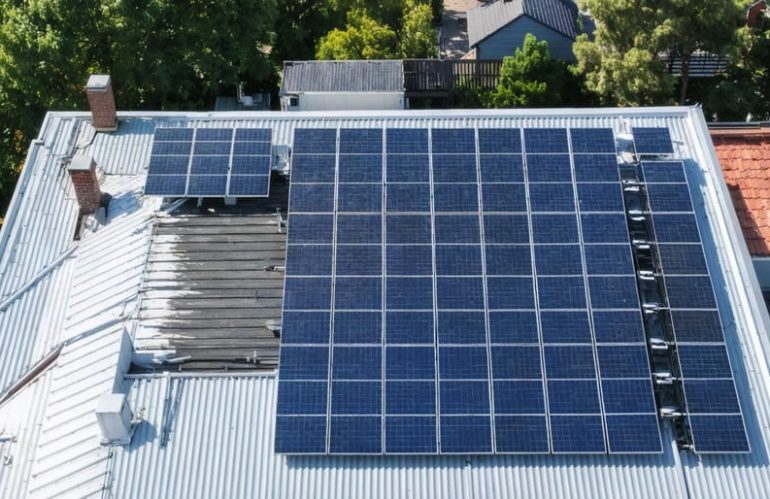
Installing solar panels requires careful attention to setback requirements – the critical spacing needed between panels and roof edges, vents, and other structures for optimal fire safety for solar installations. While these requirements may seem like minor technical details, they play a vital role in protecting your home and ensuring emergency responders can safely access your roof if needed. Most jurisdictions mandate specific minimum distances: typically 3 feet from roof ridges, 18 inches from hip or valley lines, and designated pathways for firefighter access. Understanding and following these setback guidelines not only keeps your installation code-compliant but also maximizes the long-term safety and performance of your solar investment. Working with a qualified installer who knows local requirements helps ensure your system meets all necessary spacing standards while still optimizing energy production.
Understanding Solar Fire Setbacks
What Are Solar Setbacks?
Solar setbacks are safety-required spaces between solar panels and specific areas of your roof or property boundaries. These requirements ensure proper access for firefighters during emergencies and help maintain the structural integrity of your solar installation. Think of setbacks as buffer zones that create clear pathways on your roof, typically measuring between 3 to 6 feet, depending on your local building codes.
These requirements serve multiple purposes beyond fire safety. They allow for proper ventilation, reduce the risk of fire spread, and ensure maintenance crews can safely access your panels. Many municipalities have specific setback guidelines that determine how far your solar panels must be from roof edges, ridge lines, and other structural features.
While setbacks might seem like a limitation, they’re actually an important safety feature that protects both your home and the professionals who might need to access your roof. Understanding these requirements is essential when planning your solar installation to ensure your system meets all local safety codes.
Why Setbacks Matter for Fire Safety
Fire setbacks play a crucial role in ensuring the safety of both your home and the firefighters who might need to access your roof during an emergency. These designated clear spaces around your solar panels create essential pathways that allow first responders to move safely across your roof, carry their equipment, and effectively combat any fires that might occur.
Think of setbacks as safety corridors on your roof. They prevent fires from spreading rapidly by creating breaks in the solar panel arrangement, much like how firebreaks work in forests. These gaps also provide ventilation points that help release heat and smoke during a fire, making it easier for firefighters to control the situation.
Additionally, setbacks ensure firefighters can quickly identify and access your roof’s structural weak points and ventilation areas, potentially saving crucial minutes during an emergency response. This thoughtful design consideration helps protect both your investment in solar energy and your home’s overall safety.

Key Setback Requirements for Solar Installations
Roof Edge Setbacks
Roof edge setbacks are crucial safety features that create accessible pathways for firefighters during emergencies. Most local building codes require a minimum 3-foot setback from the roof’s edge, though some jurisdictions may require larger distances. These setbacks serve multiple purposes: they provide safe walking paths for maintenance crews, help prevent panels from becoming dislodged during strong winds, and ensure proper roof drainage.
For hip roofs (sloped on all four sides), you’ll need setbacks from all edges. On gable roofs, setbacks are typically required along the eaves but may have different requirements for the rake edges. Some municipalities allow reduced setbacks of 18 inches on smaller roofs to maximize solar coverage while maintaining safety.
It’s worth noting that edge setbacks don’t always mean lost solar potential. The roof edges often receive less sunlight due to shading from gutters and overhangs, making these areas less ideal for panel placement anyway. When planning your solar layout, work with your installer to optimize panel placement within these safety requirements.
Ridge and Valley Setbacks
Roof ridges and valleys require specific setback distances to ensure proper fire safety and ventilation. For most residential installations, a minimum 3-foot setback from the ridge is required to allow firefighters safe access and maintain proper airflow. This space serves as a vital pathway for emergency responders and helps prevent fire spread across the rooftop.
Valleys, which are the V-shaped channels where two roof slopes meet, typically need an 18-inch setback on each side. These setbacks keep solar panels away from areas where water naturally collects and flows, preventing potential water damage while maintaining clear paths for firefighters.
Some local jurisdictions may have different requirements, particularly in high-wind or heavy snow areas. For instance, areas with frequent heavy snowfall might require larger valley setbacks to accommodate snow accumulation and removal. Always check your local building codes, as they may specify different measurements based on your region’s specific needs and environmental conditions.
These setbacks, while reducing the available space for solar panels, are essential for maintaining your home’s safety and ensuring your solar installation meets all necessary requirements.
Access Pathways
Solar installations must include clear pathways that allow firefighters to safely access your roof during emergencies. These firefighter access requirements typically include three-foot-wide pathways along the roof’s edges and between solar arrays. These paths enable emergency responders to move safely, ventilate smoke, and access critical areas during fire suppression activities. Most local building codes require two clear pathways running from the roof’s edge to the ridge, plus adequate spacing around vents and skylights. When planning your solar layout, work with your installer to ensure these essential access routes are incorporated into the design, maintaining both safety compliance and optimal panel placement for energy production.
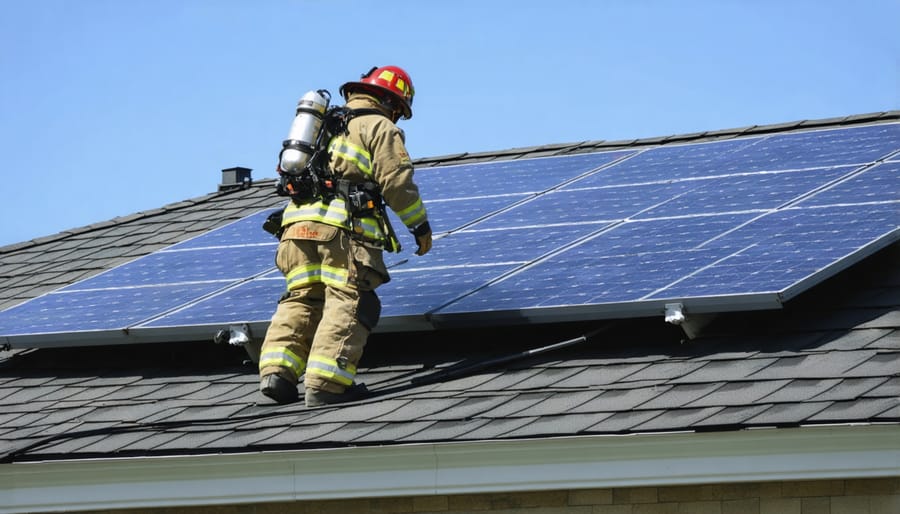

Optimizing Your Solar Layout
Working with Your Roof Design
Planning your solar panel layout while adhering to setback requirements doesn’t have to be complicated. Start by obtaining a detailed roof plan or measurements of your roof space. Mark out the required setback areas first – typically along ridges, valleys, and edges – before considering panel placement.
Look for large, unobstructed rectangular areas that remain after accounting for setbacks. These spaces are ideal for solar panel arrays. South-facing roof sections typically offer the best sun exposure in North America, so prioritize these areas when possible. If south-facing sections are limited by setbacks, east and west-facing portions can still provide good alternatives.
Consider working with multiple smaller arrays rather than one large installation if setbacks create challenging layout constraints. This approach often allows you to maximize your available roof space while maintaining all necessary safety clearances. Some homeowners find that spacing panels in two or three separate groups actually works better for their roof design than trying to force a single large array.
Remember that equipment like inverters and safety disconnects also need appropriate clearance space. Plan their locations early in the design process to ensure they don’t conflict with panel placement or setback requirements. Working with an experienced solar installer can help you optimize your layout while meeting all safety standards.
Maintaining Efficiency Within Safety Limits
While following setback requirements is essential, there are several ways to maximize your solar system’s efficiency within these safety parameters. Start by working with your solar installer to optimize panel placement, utilizing available roof space that meets setback requirements. Modern high-efficiency panels can help you generate more power from a smaller area, making the most of your limited space.
Consider a dual-orientation layout, where some panels face south while others face east or west. This arrangement can help you maintain strong energy production throughout the day while working within setback constraints. Additionally, microinverters or power optimizers can help each panel perform at its peak, regardless of its position on your roof.
If roof space is particularly limited due to setbacks, explore alternative mounting solutions. Ground-mounted systems can offer more flexibility in placement and orientation, while solar awnings or pergolas can create dual-purpose installations that generate power while providing shade.
Regular maintenance of your solar array is crucial for maintaining efficiency. Keep panels clean and ensure surrounding trees are properly trimmed to prevent shading. This becomes even more important when working with limited space due to setbacks, as every panel needs to perform optimally.
Remember that while setbacks may seem restrictive, they’re designed to protect your home while allowing for effective solar power generation. With proper planning and modern technology, you can achieve excellent energy production while maintaining all necessary safety measures.
Professional Installation and Compliance
When it comes to solar panel installation, working with qualified professionals isn’t just a recommendation—it’s essential for your safety and peace of mind. Licensed solar installers bring extensive knowledge of local fire codes, setback requirements, and safety regulations to ensure your system meets all necessary standards while helping to protect your solar investment.
Professional installers understand the complexities of roof structure, electrical systems, and fire safety requirements. They’ll conduct thorough assessments of your roof layout, ensuring proper placement of panels with adequate setbacks for firefighter access. They’ll also verify that your installation complies with local building codes and obtain necessary permits.
Quality installers will:
– Evaluate your roof’s structural integrity
– Design systems that incorporate required setback spaces
– Install proper mounting hardware and safety equipment
– Ensure appropriate electrical connections and grounding
– Provide documentation for building inspectors
– Coordinate with local fire departments when needed
By choosing certified professionals, you’re not just getting an installation—you’re getting expertise that ensures your solar system is both safe and efficient. Many installers also offer warranties and ongoing maintenance support, giving you additional confidence in your system’s long-term performance and safety compliance.
Remember to verify your installer’s credentials, including licenses, certifications, and insurance coverage. Ask about their experience with local fire codes and request references from previous installations in your area.
Proper solar setbacks are crucial for ensuring both the safety and efficiency of your solar installation. By following these guidelines, you’re not just protecting your home and family – you’re also optimizing your system’s performance and maintaining good relationships with your neighbors. Remember to work with qualified solar installers who understand local regulations and can help you design a system that meets all safety requirements. While setback requirements might seem like an extra step in your solar journey, they’re an essential investment in your home’s long-term safety and energy independence. With careful planning and proper implementation, you can enjoy the benefits of clean, renewable energy while maintaining peace of mind about your installation’s safety and compliance.









