Solar energy’s long-term impact extends far beyond immediate power generation, creating lasting positive changes for both homeowners and the environment. As we witness the environmental benefits of solar energy unfold, research shows that solar installations can increase property values by an average of 4.1% while significantly reducing carbon emissions over their 25-30 year lifespan. Beyond individual benefits, solar farms contribute to ecosystem diversity by creating wildlife corridors…
Category: Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Environmental benefits, sustainability aspects, and climate impact
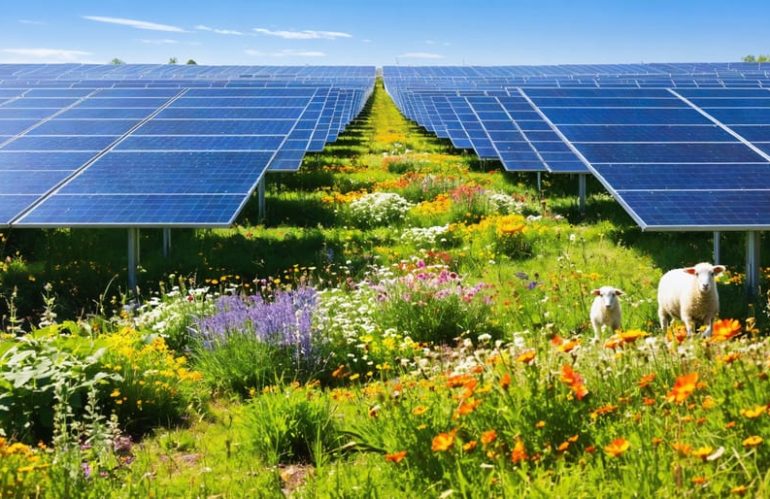
Solar Farms Transform Wasteland into Thriving Green Ecosystems
Nature’s most efficient solar collectors aren’t panels – they’re living ecosystems that transform sunlight into biomass with remarkable speed and precision. From algal blooms that double their mass daily to fast-growing bamboo forests that sequester carbon at unprecedented rates, these natural powerhouses demonstrate how the environmental benefits of solar farms can be enhanced by mimicking nature’s design. Recent research reveals that integrating…
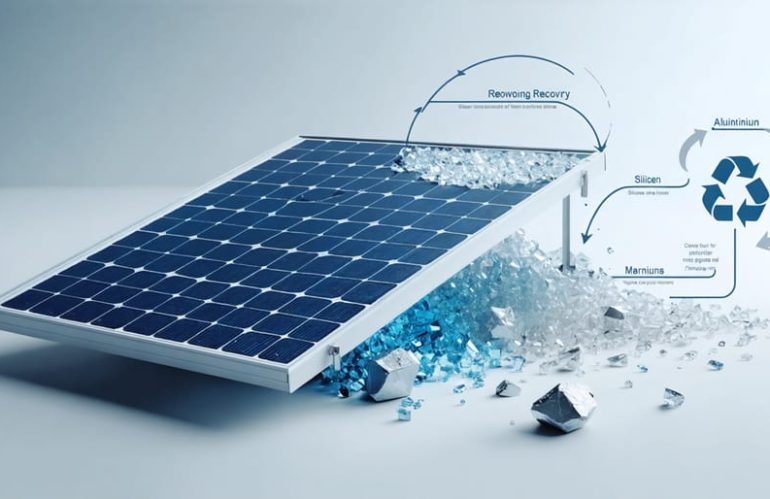
Real Solar Panel Recycling Costs: What Homeowners Need to Know
Recycling solar panels typically costs between $15-45 per panel for standard residential units, though prices vary significantly based on location and panel type. As solar installations surge nationwide, understanding these disposal and recycling challenges becomes crucial for homeowners planning their long-term solar investment. While specialized recycling facilities can recover up to 95% of panel materials, including valuable silver and silicon, the current …
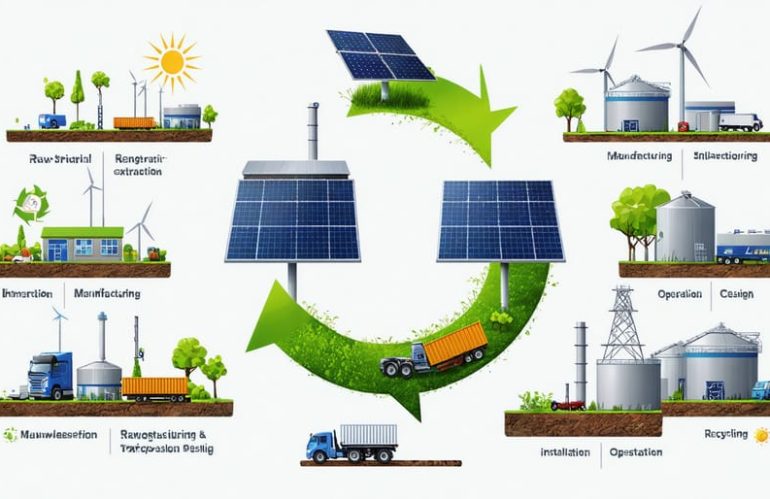
Solar Panel Life Cycle: What Every Homeowner Should Know About Manufacturing Impact
As solar panels increasingly power our transition to renewable energy, understanding their complete environmental impact requires examining more than just their clean electricity generation. From raw material extraction to end-of-life recycling, solar panels’ life cycle tells a complex story of energy investment, resource consumption, and long-term sustainability. This comprehensive analysis reveals that while manufacturing solar panels does create an initial carbon footprint, most panels offset their environmental impact within 1-4 years of operation, going on to provide decades of clean energy production.
Modern solar panels…
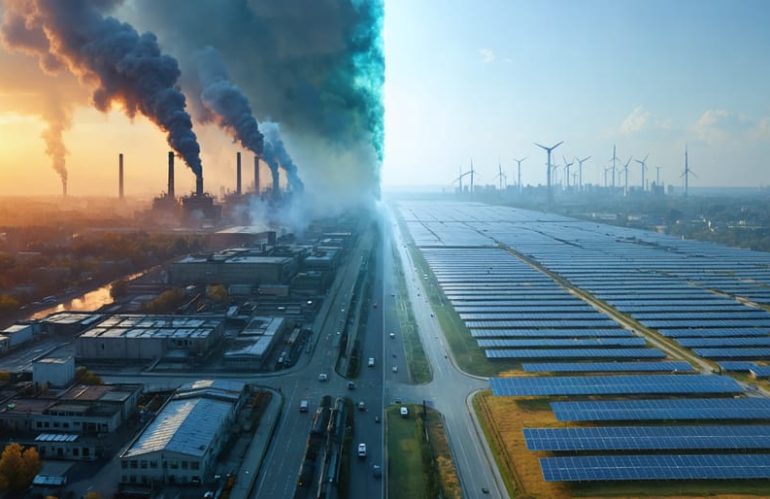
Solar Panels: How Green Are They Really? The Truth About Environmental Impact
Solar energy stands at the forefront of our transition to sustainable power, yet its environmental impact extends far beyond simply reducing carbon emissions. As homeowners increasingly turn to solar panels to power their homes, understanding both the benefits and challenges of this technology becomes crucial for making informed decisions about our energy future.
While solar power dramatically reduces greenhouse gas emissions and water consumption compared to traditional energy sources, its manufacturing process and land use requirements present important considerations. The production of solar panels involves mining raw materials …
Solar Panel Production: The True Environmental Cost Behind Your Clean Energy
Solar panels represent a crucial solution in our fight against climate change, yet their production process raises important environmental considerations. While the environmental impact of solar technology involves significant resource extraction and energy consumption during manufacturing, these initial costs are typically offset within 1-4 years of clean energy production.
Understanding this balance is essential for homeowners and environmentally conscious consumers considering solar …
Solar Panels Transform Your Home Into an Environmental Powerhouse
Solar energy stands as one of humanity’s most powerful tools in the fight against climate change, offering a clean alternative that transforms how we power our homes and communities. The environmental impact of solar power extends far beyond simple carbon reduction, creating a ripple effect of positive change across our ecosystem. Every solar panel installed represents approximately 20 metric tons of carbon emissions prevented over its lifetime – equivalent to …
Solar Sustainability: How Green are Solar Panels Really?
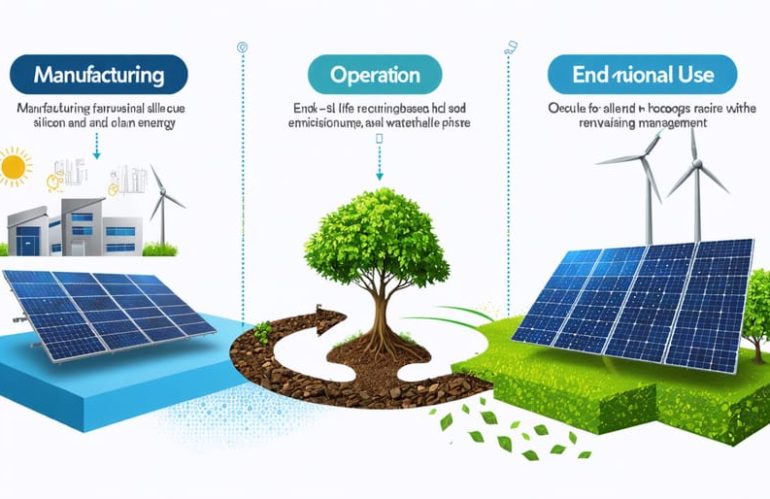
The Solar Panel Lifecycle
Manufacturing Impact
The production of solar panels requires energy, water, and raw materials, which leaves an environmental footprint. However, this impact is significantly lower than that of fossil fuels. Manufacturing solar panels uses silicon, glass, and metals like aluminum and copper. The process involves mining, refining, and assembling these materials, which consumes energy and water. Most of this energy currently comes from fossil fuels, …
How Recycling Solar Panels in the USA is Powering a Greener Future
As solar energy gains popularity in the USA, the question of what happens to panels at the end of their lifespan becomes increasingly pressing. Solar panel recycling is a critical aspect of sustainable energy management that is often overlooked, despite its potential to reduce waste, conserve resources, and minimize the hidden cost of solar panels. In this article, we will explore the current state of solar panel recycling in the USA, its importance for the environment and economy, and the challenges and …
Solar Energy Word Game That Powers Up Your Green Knowledge
Ready to supercharge your essential solar energy knowledge through an engaging word challenge? Based on the popular password game template for teachers, this interactive quiz transforms complex solar terminology into bite-sized, memorable concepts.
Test your solar expertise while having fun with carefully crafted questions covering everything from photovoltaic basics to advanced renewable energy concepts. …