Assess your home’s solar potential by evaluating your roof’s size, slope, and sun exposure. Determine your energy needs and goals, considering your current usage and future plans. Choose high-quality, efficient solar panels and inverters from reputable manufacturers, and work with a trusted installer to ensure proper system sizing and design. By taking these critical steps before going solar, you can maximize the benefits of your residential solar system and enjoy clean, affordable energy for years to come.
Understanding Your Energy Needs
Analyzing Past Utility Bills
Analyzing your past utility bills is a crucial step in estimating your solar energy needs. Gather your electricity bills from the past 12 months to get a clear picture of your annual energy usage patterns. Look for the total kilowatt-hours (kWh) consumed each month, which will help you determine your average daily consumption. Keep in mind that your usage may fluctuate throughout the year due to seasonal changes and other factors. By understanding your historical energy consumption, you can more accurately size your solar system to meet your specific needs and maximize your savings potential. Don’t worry if the process seems daunting at first—with a little organization and some simple calculations, you’ll be well on your way to designing the perfect residential solar system for your home.

Accounting for Future Changes
When designing your residential solar system, it’s essential to consider potential future changes in your energy needs. If you plan to purchase an electric vehicle (EV) in the coming years, factor in the additional electricity required for charging. Home additions or renovations may also increase your energy consumption, so it’s wise to size your system accordingly. On the other hand, investing in energy efficiency upgrades, such as LED lighting, energy-efficient appliances, or improved insulation, can help reduce your overall electricity demand. By anticipating these changes and discussing them with your solar installer, you can ensure that your solar system is designed to accommodate your future needs. This forward-thinking approach will help you maximize the long-term benefits of your solar investment, allowing you to enjoy clean, affordable energy for years to come.
Evaluating Your Solar Potential

Sun Hours and Shading
Solar access is crucial for maximizing the output of your residential solar system. The amount of sunlight your roof receives directly impacts the energy production of your solar panels. Ideally, your solar array should receive unobstructed sunlight for at least 6 hours per day. Shading from nearby trees, buildings, or other obstacles can significantly reduce the efficiency of your system. Even partial shading on a single panel can decrease the output of the entire array. To ensure optimal performance, consider trimming or removing trees that cast shadows on your roof. If shading is unavoidable, your solar installer can design your system to minimize the impact by using microinverters or power optimizers. These devices allow each panel to operate independently, so shaded panels don’t drag down the performance of the rest. By prioritizing solar access and mitigating shading issues, you can maximize the energy production and cost-saving benefits of your residential solar system.
Roof Orientation and Pitch
For maximum solar energy production, the ideal roof orientation is south-facing in the northern hemisphere and north-facing in the southern hemisphere. However, solar panels can still generate significant power on roofs facing east or west, with only a slight decrease in efficiency compared to the optimal direction. The angle or pitch of your roof also affects solar panel performance. Generally, the best angle for solar panels is equal to your location’s latitude. For example, if you live at a latitude of 35 degrees, a 35-degree tilt would be optimal. Most residential roofs have pitches between 15 and 40 degrees, which is well-suited for solar installations. If your roof doesn’t have the perfect orientation or pitch, don’t worry – modern solar panel systems can still harness plenty of sunlight to power your home and reduce your energy bills. Consult with a professional solar installer to assess your roof’s solar potential and design a system tailored to your needs.
Available Roof Space
When designing a residential solar system, it’s crucial to determine the available roof space for solar panels. Start by measuring the length and width of your roof sections that receive the most sunlight. Subtract areas occupied by chimneys, skylights, or other obstructions. Divide the remaining square footage by the size of your chosen solar panels to estimate the maximum number of panels your roof can accommodate. Keep in mind that solar panels are most effective when installed facing south at a 30-45 degree angle. If your roof space is limited, high-efficiency panels can help maximize your solar energy production.
Choosing the Right Equipment
Solar Panels
When it comes to solar panels for residential use, there are a few key factors to consider. The most common types of panels are monocrystalline and polycrystalline silicon. Monocrystalline panels are made from a single silicon crystal and tend to be more efficient, but also more expensive. Polycrystalline panels are made from multiple silicon crystals and are slightly less efficient but more affordable. Efficiency ratings indicate how much of the sun’s energy a panel can convert into usable electricity. Higher efficiency means more power output in less space. Most residential panels range from 15-22% efficiency. While higher efficiency is desirable, factors like roof size and budget also impact panel choice. Warranty coverage on solar panels typically includes both a product warranty against manufacturing defects and a performance warranty guaranteeing a certain power output level over 25-30 years. Reputable manufacturers usually offer product warranties of 10-12 years and performance warranties stating panels will produce at least 80-90% of their rated power after 25 years. Robust warranties provide peace of mind that your solar investment is protected in the long run.
Inverters
When designing your residential solar system, you’ll need to choose between central and micro inverters. Central inverters are more affordable and suitable for simple roof layouts, while micro inverters offer better performance and flexibility for complex installations. Pay attention to the inverter’s rating, which should match your solar array’s output. Reliability is key, so opt for reputable brands with solid warranties. Well-known inverter manufacturers like SolarEdge, Enphase, and Fronius have proven track records in the industry. While micro inverters may have a higher upfront cost, their long-term benefits in terms of energy production and system monitoring can make them a worthwhile investment. Ultimately, the right inverter choice depends on your specific needs, budget, and solar array configuration. Consult with a professional solar installer to determine the best inverter solution for your home.
Racking and Mounting
When designing your residential solar system, you’ll need to decide between roof-mounted or ground-mounted panels. Roof mounts are more common, as they maximize available space and are less expensive to install. However, ground mounts offer more flexibility in orientation and are easier to maintain. Racking systems, which hold the panels in place, come in various materials like aluminum or stainless steel. Look for durable, corrosion-resistant options that can withstand your local climate. Mounting equipment also includes clamps, bolts, and flashing to ensure a secure, weatherproof installation. Consider the aesthetics of different racking designs, as well as their compatibility with your chosen panels. Your solar installer can help you select the best racking and mounting solutions for your home’s unique needs, ensuring a safe and efficient system that will provide clean energy for years to come.
Battery Storage and Generators
Battery Backup
Incorporating a battery backup system into your residential solar design can provide numerous benefits. With energy storage, you can store excess solar energy generated during the day for use at night or during power outages. This allows you to maximize your energy independence and savings. When sizing your battery backup, consider your essential energy needs during an outage, such as powering your refrigerator, lights, and communication devices. Factor in the battery’s capacity, discharge rate, and round-trip efficiency to ensure it meets your requirements. A well-designed battery backup system can enhance your home’s resilience, reduce your reliance on the grid, and provide peace of mind during emergencies. Consult with a professional solar installer to determine the optimal battery size and configuration for your specific needs and budget.
Standby Generators
Standby generators are a reliable backup power solution for homes with solar systems. These generators run on various fuel types, such as natural gas, propane, or diesel, ensuring a steady supply of electricity during power outages or periods of low solar production. Automatic transfer switches seamlessly transition your home from solar to generator power when needed, minimizing disruption to your daily life. While standby generators require periodic maintenance, such as oil changes and filter replacements, the peace of mind they provide is invaluable. By incorporating a standby generator into your residential solar system design, you can enjoy the benefits of clean energy without compromising on reliability and comfort. With proper sizing and installation, a standby generator can complement your solar panels, ensuring that your home remains powered and your family stays safe, even during extended grid outages.
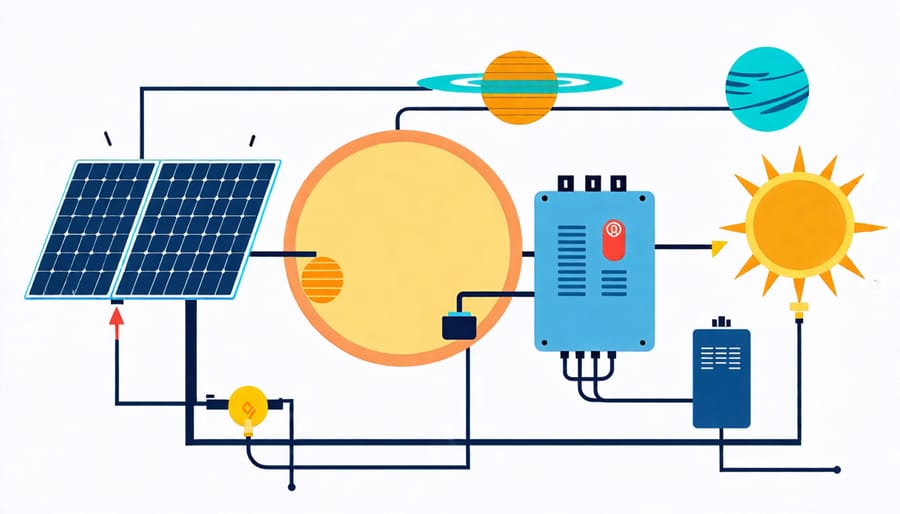
Pulling It All Together
In a complete solar system design, all the components work together seamlessly to harness the sun’s energy and convert it into usable electricity for your home. The solar panels capture sunlight and generate DC power, which is then sent to the inverter. The inverter converts this DC power into AC power that can be used by your household appliances and electronics. Any excess energy produced is either stored in batteries for later use or fed back into the grid through net metering, depending on your system’s configuration. The charge controller regulates the flow of electricity from the panels to the batteries, preventing overcharging and ensuring optimal performance. Throughout the process, the mounting system keeps your panels securely in place and positioned for maximum exposure to sunlight. By carefully selecting and integrating these components based on your specific needs and location, you can create a reliable, efficient solar power system that reduces your reliance on the grid and saves you money on energy bills for years to come. With proper installation and maintenance, your solar system will work harmoniously to provide clean, renewable energy for your home.









