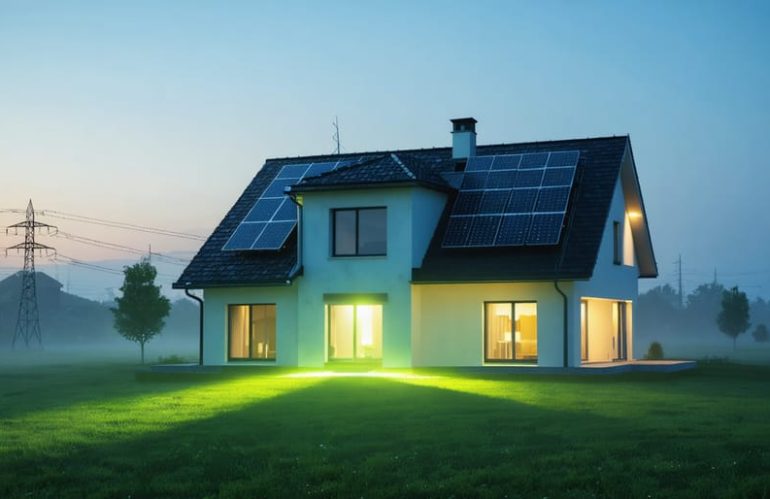
Imagine a world where your home generates, stores, and manages its own clean energy. A residential microgrid makes this sustainable vision a reality, empowering homeowners to take control of their energy consumption and costs. By integrating solar panels, battery storage, and smart energy management systems, a microgrid allows your home to operate independently from the traditional power grid. This self-sufficient energy ecosystem not only reduces your carbon footprint but also provides unparalleled energy security and resilience. In the face of power outages or natural disasters, your home remains a beacon of light and comfort. Discover how a residential microgrid can transform the way you power your life, offering a brighter, greener future for you and the planet.
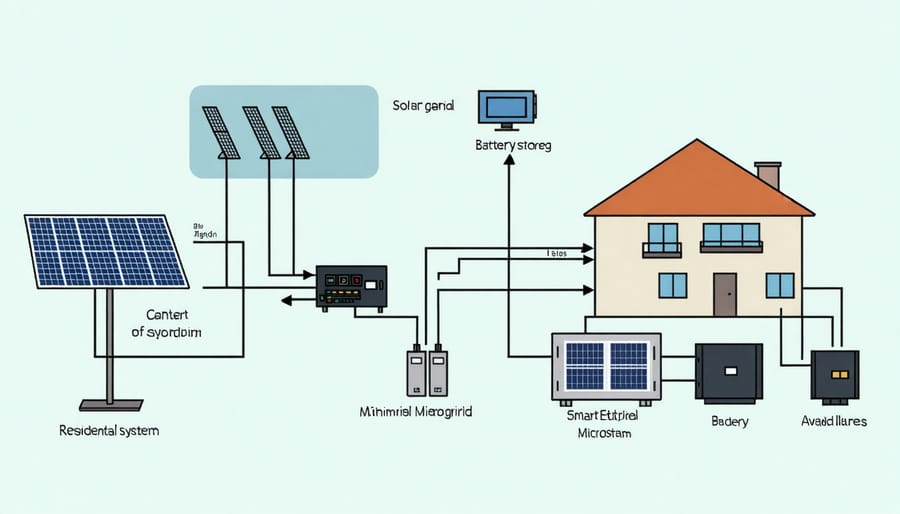
How Residential Microgrids Work
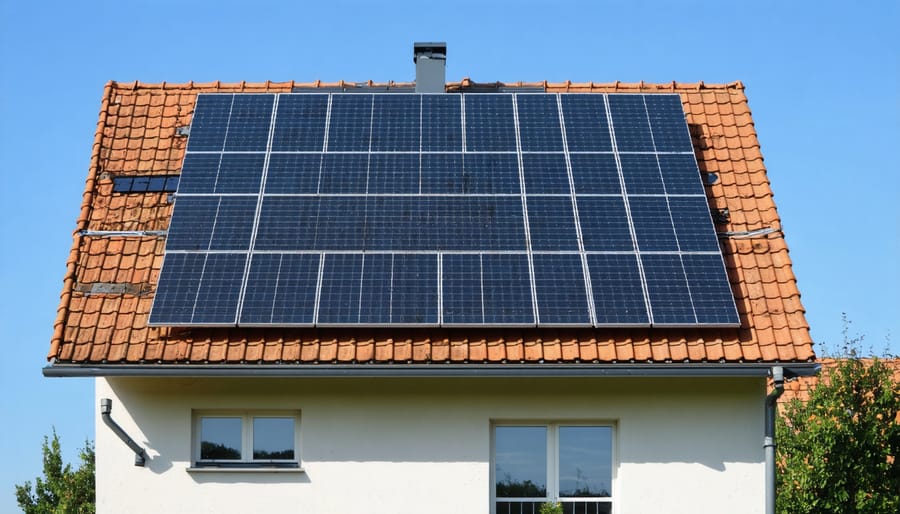
Solar Panels
Solar panels are the key component of a residential microgrid, harnessing the power of the sun to generate clean, renewable energy for your home. These panels, typically installed on your roof, convert sunlight into electricity through a process called photovoltaics. The electricity generated by the solar panels is then used to power your home’s appliances, lighting, and other electrical devices. The specific output of your solar panel system will depend on factors such as the size of your roof, the types of solar panels chosen, and your location’s solar exposure. By generating your own electricity, you can significantly reduce your reliance on the grid, lower your energy bills, and minimize your carbon footprint. Additionally, any excess energy produced by your solar panels can be stored in batteries for later use or fed back into the grid for credit on your utility bill through net metering programs.

Battery Storage
Battery storage is a crucial component of a residential microgrid, enabling homeowners to store excess solar energy generated during the day for use when the sun isn’t shining. This stored energy can power your home at night or during cloudy periods, reducing your reliance on the main grid. With solar energy storage, you can maximize the use of your solar panels and minimize the amount of electricity you need to purchase from the utility company. Battery storage also provides a backup power source during grid outages, ensuring your essential appliances and devices can continue running. As battery technology advances, the cost of energy storage is becoming more affordable, making it an increasingly attractive option for homeowners looking to optimize their microgrid’s performance and achieve greater energy independence.
Smart Control Systems
Smart control systems are the brain of a residential microgrid, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. These advanced systems continuously monitor energy production from solar panels, manage energy storage in batteries, and regulate energy usage within the home. By analyzing real-time data and predicting future energy needs, smart control systems can make intelligent decisions to balance supply and demand. They can automatically switch between energy sources, prioritize critical loads during outages, and even sell excess energy back to the grid when advantageous. With smart control systems, homeowners can maximize the benefits of their microgrid, reduce energy waste, and enjoy a more reliable and sustainable energy supply.
Benefits of a Residential Microgrid

Energy Independence and Reliability
A residential microgrid allows homeowners to generate their own clean energy, often through solar panels, and store it in batteries for later use. This setup reduces reliance on the utility grid, providing greater energy independence and reliability. In the event of a power outage, a microgrid can disconnect from the main grid and continue to supply power to the home, ensuring that essential appliances and systems remain operational. By generating and storing their own energy, homeowners can also reduce their electricity bills and minimize their carbon footprint. Microgrids are becoming increasingly popular as more people seek to take control of their energy usage and contribute to a more sustainable future. With advancements in technology and declining costs, residential microgrids are now a viable option for many homeowners looking to enhance their energy independence and reliability while supporting the transition to clean energy.
Cost Savings
Investing in a residential microgrid offers significant long-term cost savings for homeowners. By generating your own electricity through solar panels and storing excess energy in a battery system, you can reduce or even eliminate your reliance on the utility grid. This means lower monthly energy bills and protection against rising electricity rates. Plus, with net metering, you may be able to sell your excess energy back to the grid, earning credits on your utility bill. Over time, these savings can offset the initial installation costs of your microgrid system. Additionally, the energy independence provided by a microgrid can increase your home’s resale value, making it an attractive investment for eco-conscious buyers. With the potential for substantial financial benefits, a residential microgrid is a smart choice for homeowners looking to save money while embracing sustainable living.
Environmental Impact
Residential microgrids play a significant role in promoting a greener future by reducing a home’s carbon footprint. By generating and storing clean energy from renewable sources like solar panels, microgrids minimize reliance on fossil fuel-based power plants, effectively cutting down greenhouse gas emissions. This localized energy production also reduces energy losses associated with long-distance transmission, further enhancing efficiency and environmental benefits. Moreover, the ability to operate independently during grid outages ensures that homes with microgrids can continue to use clean energy even when the main grid is down, contributing to a more resilient and sustainable energy infrastructure. By adopting residential microgrids, homeowners not only reduce their environmental impact but also set an example for others to follow, paving the way for a cleaner, greener future.
Is a Residential Microgrid Right for You?
When considering whether a residential microgrid is right for your home, several factors come into play. First, evaluate your location and climate. Microgrids that incorporate solar panels are most effective in areas with ample sunlight. If your home receives consistent sun exposure, a microgrid could significantly reduce your reliance on the main grid.
Next, assess your available roof space. Solar panels require sufficient unobstructed area to generate optimal power. If your roof is small, heavily shaded, or oriented unfavorably, a microgrid may not be as efficient.
Your energy usage patterns also influence the viability of a microgrid. Homes with high electricity consumption stand to benefit more from the self-sufficiency provided by a microgrid. Review your monthly utility bills to gauge your energy needs and potential savings.
Upfront costs are another crucial consideration. While residential microgrids offer long-term savings, the initial installation expenses can be significant. Factor in the costs of solar panels, batteries, and other components, as well as any applicable incentives or financing options.
It’s essential to weigh these factors against your primary motivations for adopting a microgrid. If energy independence, environmental stewardship, and long-term cost savings are top priorities, a residential microgrid could be an excellent investment. Consult with a reputable installer to assess your home’s specific requirements and receive a personalized feasibility analysis. With careful planning and the right conditions, a microgrid can transform your home into a sustainable, resilient energy hub.
Conclusion
In conclusion, residential microgrids provide homeowners with a powerful tool to take control of their energy future. By generating clean solar power, storing it in batteries, and intelligently managing energy usage, microgrids offer increased resilience, sustainability, and potential cost savings. As we’ve seen, the benefits are numerous – from reduced reliance on the grid and lower carbon footprints to the ability to keep the lights on during outages. While the upfront investment may seem significant, the long-term advantages make residential microgrids a smart choice for forward-thinking homeowners.
If you’re interested in exploring whether a microgrid could be right for your home, the next step is to contact a reputable solar installer for a consultation. They can assess your energy needs, available space for solar panels and batteries, and provide a customized proposal outlining the costs and benefits. With expert guidance and advanced technology, you can embark on a path towards energy independence and sustainability.
As we look to the future, it’s clear that residential microgrids will play an increasingly important role in our energy landscape. By investing in this innovative solution, you can not only secure your own energy supply but also contribute to a cleaner, more resilient grid for all. The power is in your hands – take the first step today.









