As energy costs rise and power outages become more frequent, choosing the right solar battery setup can make or break your home’s energy independence. The decision between AC-coupled and DC-coupled solar storage systems impacts everything from installation costs to overall system efficiency. While both configurations can effectively store solar power for nighttime use or backup power, they operate quite differently and serve distinct needs. Modern solar installations now offer these two primary approaches to connecting batteries with your solar panels, each bringing unique advantages for specific household situations. Understanding the key differences between AC and DC coupling will help you maximize your solar investment and ensure your system meets your long-term energy goals. Whether you’re adding batteries to an existing solar setup or planning a new installation from scratch, this guide will help you make an informed choice that aligns with your home’s energy requirements and budget.
Understanding AC and DC Coupling Basics
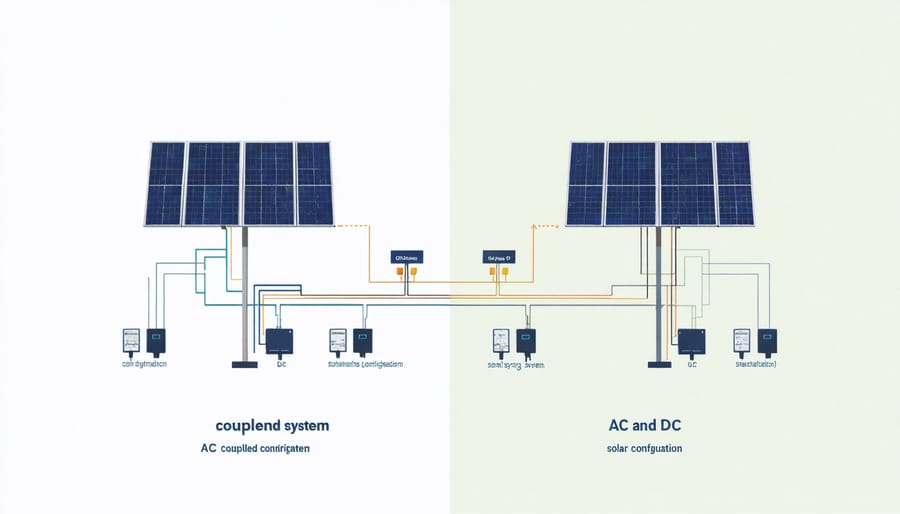
What is AC Coupling?
In an AC coupled solar system, your solar panels and battery storage operate as two separate systems connected through solar panel inverters. The setup includes a standard solar inverter that converts DC power from your panels into AC power for your home, plus a separate battery inverter that converts AC power back to DC for storage in your batteries.
Think of it like having two neighboring power stations that work together: one handles your solar production, while the other manages your battery storage. When your panels generate excess power during the day, that energy flows through both inverters before reaching your batteries. Similarly, when you need stored power at night, it passes through the battery inverter to power your home.
This arrangement is particularly popular for adding battery storage to existing solar installations, as it doesn’t require modifying your current solar setup.
What is DC Coupling?
DC coupled solar systems connect your solar panels directly to a battery system through a single hybrid inverter. In this setup, the solar energy flows straight from your panels to the battery storage in its native DC form, without any conversion steps in between. Think of it as a more streamlined path for your solar power to follow.
The main components of a DC coupled system include your solar panels, a charge controller to manage the power flow, a battery bank for storage, and a hybrid inverter that handles both battery charging and power conversion for your home use. This direct connection means less energy is lost in the process, making DC coupling slightly more efficient than its AC counterpart.
DC coupled systems are particularly effective for new solar installations, where all components can be installed together from the start. They’re also ideal for homes that primarily want to store solar energy for later use, rather than sending excess power back to the grid.
Cost Comparison: Installation and Maintenance
When comparing AC and DC coupled solar systems, the initial solar panel installation costs can vary significantly. DC coupled systems typically have a lower upfront cost because they require fewer components and have a more streamlined installation process. You can expect to pay about 10-15% less for a DC coupled system compared to an equivalent AC coupled setup.
However, the cost equation isn’t quite that simple. AC coupled systems often prove more cost-effective in retrofit situations, where you’re adding battery storage to an existing solar setup. This is because you won’t need to replace your current inverter, saving thousands in equipment costs.
For maintenance, DC coupled systems generally have lower long-term costs due to their simpler design and fewer components that could potentially fail. With fewer conversion steps and connection points, there’s less that can go wrong. Annual maintenance costs for DC coupled systems typically range from $100-200.
AC coupled systems, while having more components, offer greater flexibility when it comes to repairs and replacements. If one component fails, you can often replace just that piece rather than overhauling the entire system. Annual maintenance costs for AC coupled systems usually fall between $150-300.
Labor costs for routine maintenance tend to be similar for both systems, but AC coupled systems might require slightly more time during service visits due to their additional components. However, they often make up for this with easier troubleshooting and more straightforward component replacement.
When considering long-term value, factor in that AC coupled systems typically offer more flexibility for future upgrades and system expansion. This adaptability could lead to cost savings down the road if you decide to expand your solar capacity or upgrade your battery storage.
Energy Efficiency Face-Off
Power Conversion Losses
Every time electricity is converted from one form to another, some energy is lost as heat. In AC-coupled systems, solar power goes through multiple conversions: first from DC to AC at the solar inverter, then from AC to DC to charge the battery, and finally back to AC for home use. These multiple conversion steps typically result in efficiency losses of 10-15%.
DC-coupled systems are generally more efficient because they require fewer conversion steps. Solar power flows directly from the panels to the battery in DC form, with just one conversion to AC when power is needed for home use. This streamlined process usually results in only 2-5% energy loss during conversion.
While the difference might seem small, these efficiency gains can add up over time, potentially saving you money on your energy bills and making better use of your solar generation. However, conversion efficiency is just one factor to consider when choosing between these systems.
Overall System Efficiency
When comparing real-world efficiency, DC-coupled systems typically achieve 2-3% higher overall efficiency than AC-coupled systems. This advantage comes from reducing the number of power conversions needed to store and use solar energy. While modern solar system performance continues to improve, these efficiency differences remain consistent.
However, it’s important to note that actual performance depends heavily on usage patterns and system design. DC-coupled systems perform best when solar production and battery charging occur simultaneously, while AC-coupled systems offer more flexibility for retrofitting and expanding existing installations. In everyday use, most homeowners find that both system types meet their energy needs effectively, with the slight efficiency advantage of DC-coupled systems being most noticeable in larger installations or areas with frequent grid outages.
For most residential applications, factors like installation costs, system flexibility, and local requirements often outweigh the modest efficiency difference between these configurations.

Making the Right Choice for Your Home
Best for New Installations
For new solar installations, DC-coupled systems are generally the recommended choice. These systems offer higher overall efficiency and typically cost less to install since they require fewer components. When you’re starting from scratch, you can design your system with DC coupling in mind, avoiding the need for additional inverters and reducing potential points of failure.
DC-coupled systems are particularly advantageous for new installations because they allow for a more streamlined design process. You can optimize the size of your solar panels and battery storage from the beginning, ensuring all components work together seamlessly. This approach typically results in better system performance and lower energy losses.
However, your specific situation might warrant considering AC coupling. If you’re planning to install a very large solar array or if your local regulations require certain safety features, an AC-coupled system could be more suitable. It’s worth consulting with a qualified solar installer who can assess your energy needs, roof configuration, and local requirements to recommend the most appropriate solution for your home.
Remember that while initial costs are important, long-term efficiency and maintenance requirements should also factor into your decision-making process.
Best for Existing Solar Systems
If you already have a grid-tied solar system installed on your home, AC coupling is typically your best option for adding battery storage. This approach allows you to integrate batteries into your existing setup without replacing your current solar inverter, making it a more cost-effective solution for retrofitting.
AC coupling works seamlessly with your existing solar installation because it connects to your home’s AC wiring, working alongside your current inverter rather than replacing it. This means less disruption during installation and lower upfront costs since you’re building upon your existing infrastructure rather than starting from scratch.
However, it’s worth noting that while AC coupling is generally more convenient for existing systems, it does come with slightly lower overall efficiency compared to DC coupling. Despite this small trade-off, the savings in installation costs and minimal disruption to your current setup usually make it the more practical choice for homeowners looking to add storage to their existing solar array.
Remember to consult with a qualified solar installer who can evaluate your specific system and confirm compatibility before proceeding with any modifications.
When choosing between AC and DC coupled solar systems, both options offer distinct advantages for homeowners looking to maximize their solar investment. DC coupled systems generally provide higher overall efficiency and are ideal for new installations where both solar panels and batteries are being installed simultaneously. They’re particularly cost-effective for larger systems and offer excellent performance during power outages.
AC coupled systems, on the other hand, shine in retrofit situations and offer greater flexibility in terms of component selection and system expansion. They’re typically easier to install and maintain, making them a practical choice for many homeowners, especially those adding battery storage to existing solar setups.
Your final decision should depend on your specific circumstances. Consider DC coupling if you’re installing a new system and prioritize maximum efficiency. Opt for AC coupling if you’re adding batteries to existing solar panels or value system flexibility and simpler installation. Remember to consult with qualified solar installers who can evaluate your home’s unique needs and help you make the most informed decision for your sustainable energy future.









