Transform your home into an energy fortress with a resilience zone – a revolutionary approach to power security that keeps your essential systems running even when the grid fails. By combining solar panels, smart battery storage, and automated transfer switches, resilience zones create an independent power hub within your home, ensuring critical areas like your kitchen, home office, or medical equipment never lose power. Unlike traditional whole-house backup systems, resilience zones offer a cost-effective solution by focusing on protecting what matters most.
As extreme weather events and grid instability become more common, homeowners are discovering that resilience zones provide peace of mind without the hefty price tag of full-home backup power. This innovative system seamlessly integrates with existing solar installations, automatically isolating critical circuits during outages while maintaining optimal energy flow during normal operations. Whether you’re working from home, protecting temperature-sensitive medications, or simply wanting to keep your family comfortable during emergencies, a resilience zone offers the perfect balance of reliability, efficiency, and practical energy independence.
What Makes a Resiliency Zone in Your Home Solar Setup
Essential Components
A functional resiliency zone relies on several key components working together as part of a high-performance solar home system. The foundation starts with solar panels that capture renewable energy, connected to a robust battery storage system for storing excess power. A smart inverter serves as the brain of the operation, managing power flow and seamlessly switching between grid and stored energy when needed.
Essential monitoring equipment helps track system performance and energy usage patterns, while automatic transfer switches ensure smooth transitions during outages. Advanced load management systems prioritize power distribution to critical appliances and areas of your home when operating on backup power.
Protection components like surge suppressors and circuit breakers safeguard your equipment, while weatherproof enclosures shield sensitive components from the elements. A user-friendly control interface gives homeowners easy access to system settings and performance data. Additionally, smart thermostats and energy-efficient appliances help optimize power consumption within the resiliency zone, maximizing the effectiveness of your backup power system.
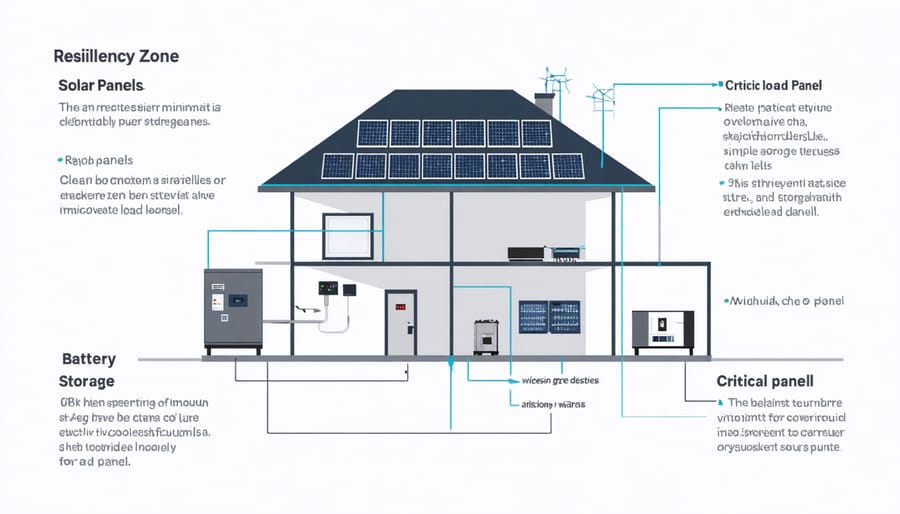
Critical Load Management
Managing your power needs during an outage starts with identifying your essential loads – the devices and appliances you absolutely need to keep running. Begin by creating a detailed list of critical items like refrigeration, medical equipment, basic lighting, and communication devices. Consider both their power requirements and usage patterns.
Once you’ve identified these loads, prioritize them based on importance and energy consumption. Medical equipment should always take top priority, followed by food preservation and basic comfort needs. A smart approach is to create tiered categories: must-have, important, and nice-to-have loads.
To effectively manage these critical loads, install a critical loads panel that connects only essential circuits to your backup power system. This ensures your backup power isn’t wasted on non-essential items during an outage. Consider using smart switches or load controllers that can automatically shed less important loads when battery levels drop below certain thresholds.
Monitor your energy usage patterns during normal operations to better understand your critical load requirements. This helps in sizing your backup system appropriately and developing effective power management strategies for outage situations.

Creating Your Home’s Power Safety Net
Planning Your Backup Circuit
Creating an effective backup circuit requires thoughtful planning to ensure your essential needs are met during power outages. Start by making a comprehensive list of critical loads – these typically include your refrigerator, lighting circuits, medical equipment, and communication devices. Consider seasonal variations too; you’ll want heating systems backed up in winter and cooling systems in summer.
Next, calculate the total wattage of these essential items. This helps determine the size of your backup system and ensures you don’t overload it. Remember to account for surge requirements, especially for appliances with motors that need extra power to start up.
To storm-proof your solar system, consider organizing your backup loads into priority tiers. Tier 1 might include absolute essentials like medical equipment and refrigeration, while Tier 2 could cover comfort items like additional lighting or entertainment systems.
Consider installing a dedicated electrical subpanel for your backup circuits. This makes installation simpler and provides a clear separation between backed-up and non-backed-up loads. It’s also wise to position this panel close to your main electrical panel to minimize wiring complexity and costs.
Finally, work with a qualified electrician to design your backup circuit layout. They can help ensure your system meets local codes and operates safely while maximizing the efficiency of your backup power solution.
Battery Integration Strategies
Integrating batteries into your resiliency zone requires careful planning to maximize both efficiency and reliability. The key is to select the right battery capacity based on your essential power needs during outages. Start by calculating your critical loads – typically including refrigeration, lighting, medical equipment, and basic communication devices.
Modern lithium-ion batteries offer the best balance of performance and longevity for most homeowners. Position your batteries in a temperature-controlled, ventilated space, ideally close to your main electrical panel to minimize power losses. Consider installing multiple smaller batteries rather than one large unit to enhance system reliability and allow for future expansion.
Smart battery management systems help optimize charging cycles and extend battery life. Program your system to prioritize battery charging during off-peak hours when electricity rates are lower. During normal operation, your batteries should maintain a 20-30% reserve capacity specifically for unexpected outages.
For maximum effectiveness, integrate your battery storage with smart home technologies. This allows automated load shedding during outages, ensuring your stored energy powers only essential devices. Many systems now offer smartphone monitoring, letting you track battery levels and energy consumption in real-time.
Remember to schedule regular maintenance checks and keep your batteries within their recommended temperature range (usually 50-85°F) for optimal performance and longevity. With proper integration, your battery system becomes the backbone of a reliable resiliency zone.
Smart Management of Your Resiliency Zone
Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular maintenance of your resiliency zone is essential for ensuring reliable backup power when you need it most. Schedule monthly visual inspections of your battery system, inverters, and critical load panel. Check for any loose connections, signs of wear, or unusual sounds that might indicate potential issues.
Keep a maintenance log to track system performance and schedule professional check-ups every six months. During these check-ups, a qualified technician should test battery capacity, verify inverter settings, and ensure all components are functioning optimally. They’ll also clean any dust or debris that might affect system efficiency.
Monitor your system’s performance through its mobile app or web interface daily. Pay attention to battery charge levels, power consumption patterns, and any alert notifications. This proactive approach helps identify potential problems before they become serious issues.
Don’t forget to test your automatic transfer switch quarterly by simulating a grid outage (under professional supervision). This ensures your system will respond correctly during actual power failures. Regular maintenance not only extends your system’s lifespan but also maximizes your investment in energy independence.
Automated Controls
Modern resiliency zones employ smart technology to seamlessly manage power distribution throughout your home. Automated control systems act as the brains of your setup, constantly monitoring energy production, storage levels, and household consumption. These intelligent systems automatically switch between power sources – grid, solar, and battery – to maintain optimal efficiency and ensure continuous power supply.
When grid power fails, the automated controls instantly activate your backup system, redirecting stored energy to your essential circuits. This happens so quickly that you might not even notice the transition. Smart load management features prioritize critical appliances while reducing power to non-essential items, helping your stored energy last longer during outages.
Many systems now offer user-friendly smartphone apps that let you monitor and control your resiliency zone remotely. You can track real-time energy usage, adjust settings, and receive alerts about system status or potential issues. Some advanced systems even use weather forecasts to optimize energy storage, ensuring you’re prepared for upcoming storms or grid disruptions.
These automated controls not only provide peace of mind but also help maximize your energy savings during normal operation by intelligently managing power flow between your solar panels, battery storage, and home appliances.

Real Benefits of a Well-Planned Resiliency Zone
Energy Independence
A key feature of resiliency zones is their ability to provide reliable power during grid outages, effectively creating a mini off-grid solar system when needed. These zones combine solar panels, battery storage, and smart inverters to maintain power to essential appliances and systems even when the main grid fails.
During outages, the resiliency zone automatically isolates itself from the main grid and switches to island mode. This seamless transition ensures that critical loads like refrigerators, medical equipment, and communication devices continue running without interruption. The system prioritizes power distribution based on pre-set preferences, directing energy to the most important needs first.
Battery storage plays a crucial role in maintaining power reliability. During normal operation, excess solar energy charges the batteries, creating an energy reserve for nights and cloudy days. Smart energy management systems monitor consumption patterns and weather forecasts to optimize battery charging and usage, ensuring maximum efficiency and reliability when grid power isn’t available.
What sets resiliency zones apart is their ability to function both as part of the larger grid and independently. This flexibility not only provides peace of mind during outages but also helps reduce daily energy costs through strategic power management and solar generation.
Cost Savings
Implementing a resiliency zone in your home can significantly save on energy costs while providing crucial backup power during emergencies. The initial investment typically pays for itself through multiple financial benefits. During normal operations, your resiliency zone reduces daily electricity consumption by efficiently managing power distribution to essential appliances and systems.
Most homeowners see a 20-30% reduction in their monthly utility bills after implementing a resiliency zone strategy. This savings comes from smart load management and the ability to prioritize power usage during peak rate periods. During power outages, the financial benefits become even more apparent, as you avoid costs associated with food spoilage, business interruption for home offices, and potential property damage from system failures.
Insurance companies often offer reduced premiums for homes with resilient power systems, recognizing their reduced risk profile. Additionally, many utility companies provide rebates and incentives for implementing resiliency measures, further offsetting the initial setup costs.
The long-term value proposition extends beyond immediate savings. A well-designed resiliency zone increases property value and reduces dependency on grid power during price spikes. Many homeowners report complete investment recovery within 3-5 years through combined savings from reduced energy consumption, lower insurance costs, and avoided emergency expenses.
Creating a resiliency zone in your home represents a significant step toward energy independence and environmental responsibility. By implementing the strategies and components we’ve discussed, you’re not just protecting your home from power outages – you’re investing in a sustainable future while potentially reducing your energy costs.
Remember that your resiliency zone can start small and grow over time. Begin with essential circuits and gradually expand based on your needs and budget. The key is to prioritize what matters most to your household and design your system accordingly.
The benefits of establishing a resiliency zone extend beyond personal convenience. You’re contributing to grid stability, reducing carbon emissions, and setting an example for your community. As extreme weather events become more common and grid reliability concerns grow, having a resilient home energy system isn’t just a luxury – it’s becoming a necessity.
Take action today by assessing your home’s critical power needs and consulting with qualified professionals who can help design your ideal resiliency zone. Consider starting with a basic backup system and adding smart technology and renewable energy sources as you become more comfortable with the technology.
With proper planning and implementation, your resiliency zone will provide peace of mind, energy security, and financial savings for years to come. The future of home energy is resilient, sustainable, and within your reach.









