Transform your home’s energy landscape by learning how to power your home with a microgrid—a revolutionary system that combines solar panels, battery storage, and smart controls to create a self-sustaining power network. As extreme weather events and grid outages become more common, microgrids offer homeowners unprecedented energy independence and reliability. These autonomous energy systems seamlessly integrate with existing power infrastructure while providing critical backup power during emergencies, reduced electricity bills, and a smaller carbon footprint. Beyond individual benefits, microgrid installations are reshaping neighborhood energy dynamics, enabling communities to share power resources and creating resilient local energy networks that benefit everyone. Whether you’re looking to enhance your home’s energy security, reduce utility costs, or contribute to a more sustainable future, understanding microgrid installation is your first step toward energy autonomy.
What Makes a Home Microgrid Different from Traditional Solar
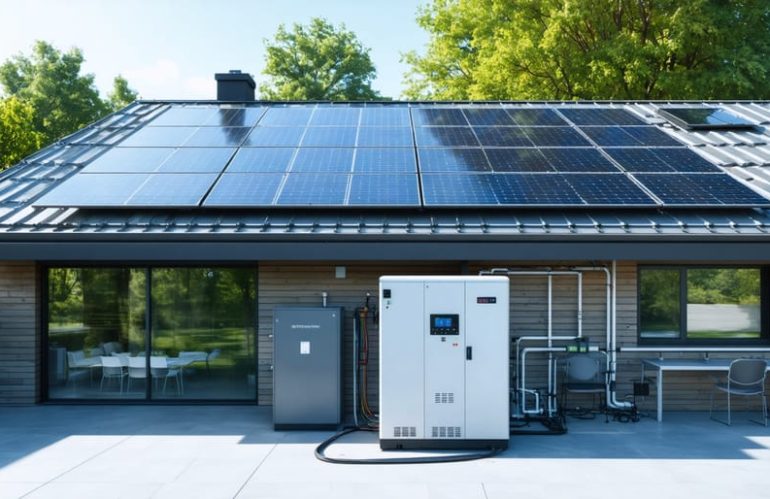
Core Components of a Home Microgrid
A home microgrid consists of several key components working together to create a reliable and efficient energy system. At its heart is the microgrid controller, which acts as the brain of the system, managing power flow and making smart decisions about when to use, store, or sell energy. Energy storage, typically in the form of batteries, allows you to keep excess power for later use, especially during outages or peak pricing periods.
Smart switches and automated transfer equipment ensure seamless transitions between grid power and your microgrid, while protecting your home’s electrical system. The distribution panel, upgraded to handle bi-directional power flow, connects all these components and your home’s circuits. Energy generation sources, such as solar panels or small wind turbines, provide the clean power that feeds your microgrid.
Modern microgrids also include monitoring systems that let you track energy usage and system performance through user-friendly apps. These smart features help you optimize energy consumption and maximize savings. While each component plays a crucial role, they work together as an integrated system to provide reliable, clean power while reducing your energy bills.

Beyond Basic Solar: The Power of Independence
While independent solar panels are an excellent starting point for sustainable living, microgrids take energy independence to the next level. Think of a microgrid as your personal power ecosystem – it’s not just about generating electricity, but also managing and storing it intelligently.
Unlike traditional solar setups that shut down during grid outages, microgrids keep your power flowing when the main grid fails. This means your lights stay on, your refrigerator keeps running, and your home remains comfortable during blackouts or severe weather events.
What makes microgrids truly revolutionary is their ability to make real-time decisions about your power usage. They can automatically switch between solar, battery storage, and grid power to optimize your energy consumption and costs. During peak rate periods, your microgrid can prioritize stored solar energy, while drawing from the grid when rates are lowest.
This independence also means you’re better protected against rising utility costs and grid instability. Many homeowners report feeling more secure knowing they have control over their energy future, while contributing to a more resilient and sustainable community power network.
Real Benefits of Installing a Microgrid
Enhanced Power Reliability
One of the most compelling benefits of a microgrid system is its ability to keep your power running when the main grid fails. Unlike traditional backup generators, microgrids seamlessly switch to island mode during outages, maintaining uninterrupted power to your home or facility. This transition happens automatically within milliseconds, so you might not even notice when the main grid goes down.
Microgrids achieve this enhanced reliability through a sophisticated combination of local power generation (typically solar panels), energy storage systems, and smart controls. During normal operations, your microgrid stays connected to the utility grid, but when an outage occurs, it instantly isolates itself and continues powering your essential loads using stored energy and ongoing renewable generation.
This self-sufficient operation proves invaluable during extreme weather events, natural disasters, or scheduled maintenance outages. For homeowners, this means keeping critical systems running – from refrigeration and heating to medical equipment and home offices. The system can maintain power for hours or even days, depending on your storage capacity and energy usage patterns, providing peace of mind and protection against increasingly common grid disruptions.

Smart Energy Management
Smart energy management is at the heart of what makes microgrids so efficient. These systems use advanced software and automation to continuously monitor and optimize power flow between your solar panels, battery storage, and home appliances. Think of it as having a smart assistant that automatically decides when to store excess solar power, when to use grid electricity, and when to tap into your batteries.
The system learns your household’s energy consumption patterns and adapts accordingly. During peak solar production hours, it might prioritize charging your batteries while running energy-intensive appliances. When electricity rates are high, it can switch to stored power, helping you avoid costly peak-hour charges.
Weather forecasting integration allows your microgrid to prepare for upcoming cloudy days by ensuring batteries are fully charged. The system can also automatically prioritize critical loads during power outages, ensuring your essential appliances stay running while conserving battery life.
Many modern microgrid systems come with user-friendly mobile apps that let you monitor and adjust settings from anywhere, giving you complete control over your home’s energy usage while maximizing savings and efficiency.
Financial Advantages
Installing a microgrid can lead to significant financial benefits for homeowners. The most immediate advantage is reduced utility bills through optimized energy consumption and storage capabilities. During peak rate periods, you can switch to stored power, avoiding high-cost grid electricity. Many utility companies offer net metering programs, allowing you to sell excess energy back to the grid, creating a new revenue stream.
The system’s smart technology automatically selects the most cost-effective power source, whether it’s solar, stored energy, or grid power, maximizing your savings. Additionally, microgrids protect against costly power outages, which can lead to food spoilage, business interruption, or damage to sensitive equipment. Federal and state incentives, including tax credits and rebates, can significantly offset initial installation costs.
Over time, as electricity rates continue to rise, your microgrid investment becomes increasingly valuable, offering long-term financial stability and protection against future utility price hikes.
Installation Process Made Simple
Planning Your Microgrid
Before installing a microgrid, careful planning is essential to ensure your system meets your energy needs effectively. Start by assessing your current energy consumption patterns and future requirements. This includes analyzing your monthly electricity bills, identifying peak usage times, and considering any planned additions to your home that might affect energy demand.
Next, evaluate your property’s potential for renewable energy generation. Consider factors like available roof space for solar panels, local wind patterns, or even the possibility of small-scale hydroelectric power if you have access to flowing water. A professional energy consultant can help you determine the most viable options to transform your home into an energy-independent powerhouse.
Your microgrid design should also account for battery storage capacity, which will determine how long you can operate independently from the main grid. Consider factors like weather patterns, backup power needs, and whether you want to sell excess energy back to the utility company.
Don’t forget to check local regulations, permitting requirements, and utility interconnection policies. Some areas offer incentives for microgrid installations, while others may have specific requirements for system design and safety features. Working with a qualified contractor who understands these regulations will ensure a smooth planning process.
Integration Steps
The integration of a microgrid system into your home follows a straightforward process that typically takes about 2-3 weeks from start to finish. First, professional installers conduct a thorough site assessment, evaluating your current power setup and identifying the best locations for new equipment. They’ll then design a custom system that meets your specific energy needs and goals.
Next comes the installation of core components, starting with the smart controller – the brain of your microgrid. This is followed by setting up the battery storage system, which is typically placed in your garage or utility room. The team then installs the automatic transfer switch, which seamlessly transitions between grid power and your microgrid system.
The integration phase involves connecting your existing solar panels (if you have them) or installing new ones, along with linking all electrical components to your home’s main electrical panel. Advanced monitoring systems are then set up to track your energy production and usage in real-time.
Finally, the system undergoes extensive testing to ensure everything works correctly and safely. Your installer will provide training on how to monitor and manage your new microgrid through a user-friendly app or control panel, empowering you to maximize your energy independence.
Smart Features and Future-Proofing
Automation Capabilities
Modern microgrids come equipped with sophisticated automation features that make managing your home’s energy both effortless and efficient. These smart systems continuously monitor your energy production, storage, and consumption in real-time, automatically adjusting power flow to optimize efficiency and savings.
The automation system can seamlessly switch between different power sources based on availability and cost. For example, during peak utility rate hours, it can automatically draw power from your battery storage instead of the grid. When severe weather approaches, the system can prepare by fully charging batteries and adjusting power distribution to critical home systems.
Through user-friendly mobile apps and smart home integration, you can monitor your microgrid’s performance from anywhere. These interfaces provide easy-to-understand visualizations of your energy usage patterns, solar production, and battery levels. You can set custom preferences for how your system operates, such as prioritizing stored energy use during specific times or maintaining minimum battery reserves for emergencies.
The system also sends automated alerts about maintenance needs, potential issues, or opportunities to optimize your energy usage, ensuring your microgrid operates at peak efficiency year-round.
Expansion Options
A microgrid system can grow alongside your energy needs, offering numerous expansion possibilities for the future. One popular upgrade option is increasing battery storage capacity, allowing you to store more excess energy for extended periods of power independence. You can also add more solar panels to generate additional power, or integrate wind turbines for diversified energy generation.
Smart home integration represents another exciting expansion pathway, enabling automated energy management through connected devices and intelligent controls. This can include smart thermostats, automated lighting systems, and energy monitoring displays that help optimize your power usage.
For those interested in complete energy independence, adding backup generators or fuel cells can provide additional reliability during extended periods of limited solar production. Electric vehicle charging stations are another valuable addition, especially as more households transition to electric transportation.
Many homeowners also choose to incorporate energy-efficient appliances and smart power strips that can be programmed to work optimally with their microgrid system, further reducing energy consumption and improving overall system efficiency. These modular expansion options ensure your microgrid can adapt to your changing energy needs while maintaining reliable power supply.
Making the Decision
Deciding whether a microgrid is right for your home involves carefully weighing several key factors. Start by assessing your energy needs and goals. Are you looking to achieve energy independence, reduce utility bills, or ensure power reliability during outages? Your primary motivation will help guide your decision-making process.
Consider your current energy consumption patterns and costs. Review your utility bills from the past year to understand your average usage and spending. If you’re already using solar panels or planning to install them, a microgrid can enhance your system’s effectiveness by storing excess energy and managing power distribution more efficiently.
Location plays a crucial role in your decision. Areas prone to power outages, natural disasters, or unreliable grid service are ideal candidates for microgrids. Additionally, check local regulations and utility policies regarding grid-connected systems, as these can impact your installation options and potential cost savings.
Evaluate your property’s physical characteristics. Do you have adequate space for battery storage and control systems? Is your electrical system up to date and compatible with microgrid technology? A professional energy assessment can help answer these questions and identify any necessary upgrades.
Financial considerations are equally important. While microgrids require significant upfront investment, factor in available tax incentives, rebates, and long-term energy savings. Calculate your expected return on investment, including reduced utility bills and potential earnings from selling excess power back to the grid.
Remember, a microgrid is a long-term investment in your home’s energy future. If reliability, sustainability, and energy independence align with your goals, and the financial numbers make sense, a microgrid could be an excellent choice for your home.
Installing a microgrid system represents a significant step toward sustainable living and energy independence made easy. The benefits of microgrids extend far beyond just backup power during outages. By implementing a microgrid system, homeowners can enjoy reduced energy costs, increased property value, and greater control over their energy consumption while contributing to a cleaner environment.
As you consider taking the next step toward microgrid installation, remember to start with a professional energy assessment of your property. This will help determine the optimal system size and configuration for your specific needs. Connect with certified installers who can provide detailed quotes and timeline estimates, and don’t forget to research available incentives and tax credits in your area to maximize your investment.
The transition to microgrid technology may seem daunting at first, but with proper planning and professional guidance, it’s a achievable goal for most homeowners. As energy storage technology continues to advance and installation costs decrease, microgrids are becoming increasingly accessible to residential consumers.
Take action today by scheduling consultations with local installers and beginning your journey toward energy independence. Your future self will thank you for making this smart, sustainable choice for your home and the environment.